* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mutation, repair, and recombination
Holliday junction wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
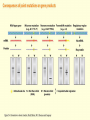
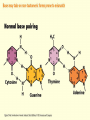
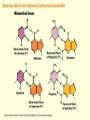
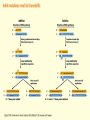
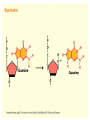
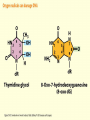
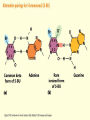
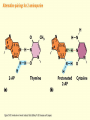
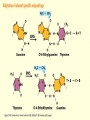
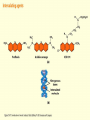
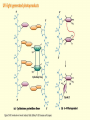
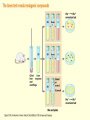
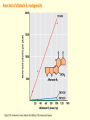
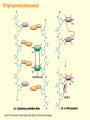
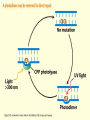
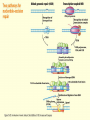
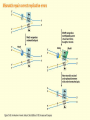
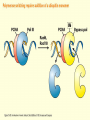
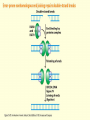
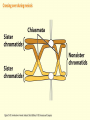
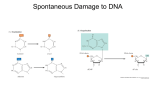
Chapter 16 Mutation, Repair and Recombination Question Lysine and arginine are two amino acids with similar sized “R” (side-) groups and similar biochemical behavior (for example, both are basic residues). A mutation results in substitution of lysine for arginine and has no detectable effect on the function of that protein. Which statement best applies to this situation? •The mutation is a silent mutation. •The mutation is a frameshift mutation. •The amino acid change is conservative. •The amino acid change is silent. •This organism displays no codon bias. Question Which of the following represents a correct or acceptable phrase in genetics? • Mutant protein • Protein mutation • DNA mutation • A and C • All of the above Question Which of the following statements is correct about the bases in DNA under normal circumstances: • Adenine should pair with thymine. • The bonds holding guanine and cytosine together are stronger than the bonds holding adenine and thymine together. • A purine always binds to a pyrimidine. • A substitution of adenine for guanine is a transition mutation. • All of the above Carcinogens and the Ames Test Repair mechanisms Photo reactivation repair Base excision repair Nucleotide excision repair Transcription coupled repair Mismatch repair Undamaged DNA UV light (mutagenic agent) EMS, NG (mutagenic agent) Pyrimidine dimers Methylated base Visible light Alkyl Transferase Photolyase Original Base Inactivated after action Replication dependent repair Question Which of the following repair pathways do not involve the use of a homology-dependent repair system? a. Base excision repair b. Photo reactivation repair c. Transcription coupled repair d. Nucleotide excision repair e. Mismatch repair Question •Which of the following DNA duplexes is most stable? 5’ AATTAATTAATTAATTAATT 3’ 3’ TTAATTAATTAATTAATTAA 5’ 5’ GGCCGGCCGGCCGGCCGGCC 3’ 3’ CCGGCCGGCCGGCCGGCCGG 5’ 1. Both are equally stable. 2. B is more stable than A. Question Which of the following repair pathways do not involve the use of a homology-dependent repair system? a. Base excision repair b. Photo reactivation repair c. Transcription coupled repair d. Nucleotide excision repair e. Mismatch repair