* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lh6Ch05
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Paracrine signalling wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
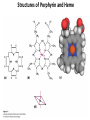
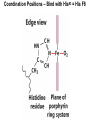
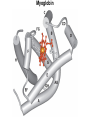
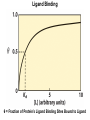
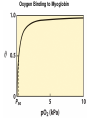
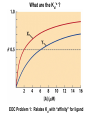
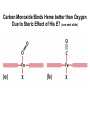
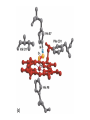
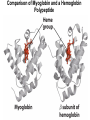
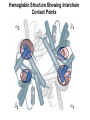
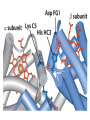
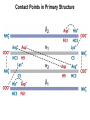
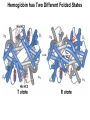
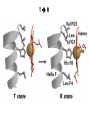
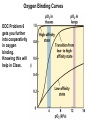
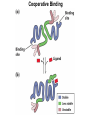
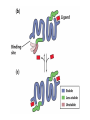
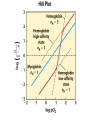
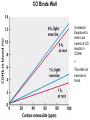
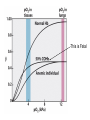
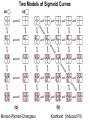
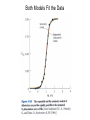
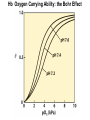
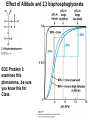
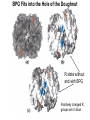
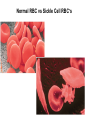
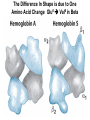
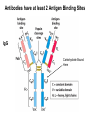
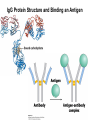
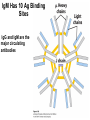
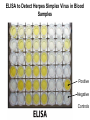
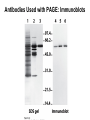
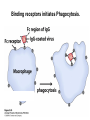
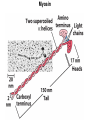
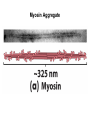
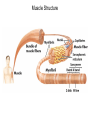
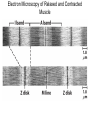
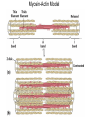
Chapter 5: Protein Function –Binding Function of Globular Proteins: Ligand Binding Learning Goals 1. Reversible binding of ligands is essential – Specificity of ligands and binding sites – Ligand binding is often coupled to conformational changes, sometimes quite dramatic (Induced Fit) – In multisubunit proteins, conformational changes in one subunit can affect the others (Cooperativity) – Interactions can be regulated 2. Illustrated by: – Hemoglobin, antibodies, and muscle contraction Functions of Globular Proteins • Storage of ions and molecules – myoglobin, ferritin • Transport of ions and molecules – hemoglobin, serotonin transporter • Defense against pathogens – antibodies, cytokines • Muscle contraction – actin, myosin • Biological catalysis – chymotrypsin, lysozyme Protein Interaction with Other Molecules • Reversible, transient process of chemical equilibrium: A + B AB • A molecule that binds to a protein is called a ligand – Typically a small molecule • A region in the protein where the ligand binds is called the binding site • Ligand binds via same noncovalent forces that dictate protein structure (see Chapter 4) – Allows the interactions to be transient Hemoglobin and Oxygen/CO2 Binding Structures of Porphyrin and Heme Coordination Positions – Bind with His93 = His F8 Myoglobin Ligand Binding θ = Fraction of Protein’s Ligand Binding Sites Bound to Ligand Oxygen Binding to Myoglobin What are the Kd’s ? A EOC Problem 1: Relates Kd with “affinity” for ligand How is the Binding Experiment Done? With proteins such as Hemoglobin and Myoglobin, the absorbance spectrum changes between free and bound protein can be measured in a spectrophotometer. The spectrum of deoxy-myoglobin is different than oxymyoglobin. What about proteins without a chromophore? and binding colorless ligands? Equilibrium dialysis Human serum transferrin binds iron at pH 7.2 with a Kd of 10-19 to 10-20 M EOC Problem 5 uses simple inspection of the data to get Kd ! Make sure you get this done before Class. Carbon Monoxide Binds Heme better than Oxygen Due to Steric Effect of His E7 (see next slide) Comparison of Myoglobin and a Hemoglobin Polypeptide Amino Acid Sequence of Myoglobin and Hemoglobin Polypeptides Grey Conserved, Pink Conserved in all known Hemoglobins Hemoglobin Structure Showing Interchain Contact Points Contact Points in Primary Structure Hemoglobin has Two Different Folded States TR Oxygen Binding Curves EOC Problem 6 gets you further into cooperativity in oxygen binding. Knowing this will help in Class. Cooperative Binding Hill Plot CO Binds Well Increased Exposure to even Low Levels of CO results in COHb! + The effect of exercise is trivial. This is Fatal Two Models of Sigmoid Curves Monod-Wyman-Changeux Koshland (Induced Fit) Both Models Fit the Data Hb Oxygen Carrying Ability: the Bohr Effect CO2 Transport on N-terminal Amino Groups Effect of Altitude and 2,3 bisphosphoglycerate EOC Problem 3: examines this phenomena...be sure you know this for Class. BPG Fits into the Hole of the Doughnut R state without and with BPG Positively charged R groups are in blue. Normal RBC vs Sickle Cell RBC’s The Difference In Shape is due to One Amino Acid Change Glu6 Val6 in Beta Separation of Protein Fragments The Classic Paper Chromatography + Electrophoresis Image from Chapter 3 Hb-S Polymerizes in the Deoxy form Lymphocytes Have Binding Proteins A Antibodies have at least 2 Antigen Binding Sites IgG Carbohydrate Bound Here IgG Protein Structure and Binding an Antigen IgM Has 10 Ag Binding Sites IgG and IgM are the major circulating antibodies Cartoon of an ELISA ELISA to Detect Herpes Simplex Virus in Blood Samples Positive Negative Controls Antibodies Used with PAGE: Immunoblots Binding receptors initiates Phagocytosis. A Myosin Myosin Aggregate Actin Filament Myosin Contacting an Actin Filament Muscle Structure Electron Microscopy of Relaxed and Contracted Muscle Myosin-Actin Model Things to Know and Do Before Class 1. Know how binding studies are done and the meaning of Kd. 2. Know how conformation of a protein affect ligand binding (models of myoglobin and hemoglobin)…for loading and off-loading oxygen. 3. How altitude affects Hb’s oxygen binding. 4. Why Hb-S causes red blood cells to change shape and what affect that has on Hb-S individuals. 5. How antibodies bind to antigens. 6. Be able to do EOC Problems 1,3, 5-7.