* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lh6Ch11aMembranes
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Paracrine signalling wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
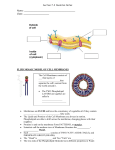
Chapter 11 Biological Membranes: Part 1 Membranes Part 1 and 2 Learning Goals: To Know – The function of biological membranes – The structure and composition membranes and their molecules – Dynamics of membranes – Structure and function of membrane proteins – Transport across biological membranes Why are TEMs of membranes always light in the middle and dark on the sides? 50 – 80 Å Thick EOC Problem 5 has to do with the length of a fatty acid: how does this play into the thickness of this membrane? Cells Are Loaded with Membranes What’s the answer to the previous thought question? Major Membrane Lipids Membrane Lipid Composition – Rat Hepatocyte Fluid Mosaic Model Lipids aggregate into structures in water • Structures formed depend on: – type of lipid – concentration • Micelles • Liposomes • Bilayers Lipids in Water EOC Problem 3 … Number of SDS moleucles/micelle. You will need to calculate the MW of dodecyl-sulfate. Asymmetric Distribution of P-lipids in Erythrocyte Membrane Membrane composition and asymmetry Membrane Asymmetry Derived in ER Functions of Proteins in Membranes • Receptors: detecting signals from outside – – – – Light (opsin) Hormones (insulin receptor) Neurotransmitters (acetylcholine receptor) Pheromones (taste and smell receptors) • Channels, gates, pumps – Nutrients (maltoporin) – Ions (K-channel) – Neurotransmitters (serotonin reuptake protein) • Enzymes – Lipid biosynthesis (some acyltransferases) – ATP synthesis (F0F1 ATPase/ATP synthase) Extraction of Membrane Proteins Glycophorin – Transmembrane Protein TetraSaccharides, N-linked Tetra-Saccharides, O-linked Six Types of Integral Membrane Proteins Bacteriorhodopsin Bacteriochlorophyll – Reaction Center Chlorophylls in Red Great Illustration of Phospholipid as a Fluid Sec A (chaperone) in blue ribbon. Cytoplasmic side with ATP (bright light) Sec YE in Cream Spacefilling cut away to show channel Transported protein in red thread Another Great Illustration of Phospholipid as a Fluid G Protein – major signaling protein, next Chapter. Phospholipid Associated with Isolated Membrane Proteins Sheep Aquaporin Fo Portion of V type Na-ATPase Hydropathy Plots Remember Hydropathic Index? Non Polar R groups have Positive Hydropathic Indices Y and W are negative Polar Amino Acids have Negative Hydropathic Indices Hydropathy Index Calculated from a Moving -Window of 7 to 20 Amino Acids Transmembrane Proteins – Positions of Y and W. Polar R – groups are Blue Y is Orange W is Red Membrane Spanning Regions can also be Beta-Barrel Structure Another Great Illustration showing the Membrane as a Fluid Surface of a B-cell showing the B-cell Receptor (purple, monovalent IgM) binding to an HIV particle. Sided Proteins Anchored by Fatty Acids (Inside) Membranes can transition from Gels to Fluids a. Gel State b. Liquid Ordered Liquid Disordered Measuring Rate of Phospholipid Mobility Membrane Lipid Movement over 56 msec EOC Problem 6 involves temperature effects on lateral diffusion in membranes. Some Membrane Proteins Have Cytoskeleton Restricted Movement Atomic Force Microscopy AFM Aquaporin from E. coli – Outside View Rafts and GPI-linked Proteins Rafts and Sea AFM Detects “Rafts” of Sphingolipids + Cholesterol Hierarchy of raft-based heterogeneity in cell membranes D Lingwood, K Simons Science 2010;327:46-50 Published by AAAS Integral Membrane Proteins Involved in Cell-Cell Communication Membrane Fusion Events, An Overview To do this, proteins have to get two membranes very close together so they touch. Caveolin Dimers form Caveloa Three Models for Protein-Induced Curvature Types of Endocytosis Influenzia Virus Must “Uncoat” in Cytoplasm Things to Know and Do Before Class 1. The major and minor membrane phospholipids. 2. Transmembrane protein structures and how they are held into the membrane. 3. Peripheral membrane proteins and how they are attached to the membrane. 4. Membrane temperature driven transitions. 5. What AFM tells us about membrane structure. 6. Membrane fusions + formation of endosomes. 7. EOC Problems: 3, 5, 6 (Hint need to calc SDS mole wt 288 Daltons)