* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Oxidative phosphorylation
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium in biology wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
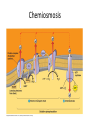
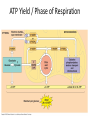
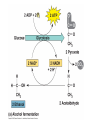
Oxidative phosphorylation • Oxidative Phosphorylation: electron transport chain and chemiosmosis • e- trasport chain embedded in INNER mito membrane • Composed of 3 transmembrane H+ pumps • Electrons flow through e- chain – Loss of energy from e-s powers H+ pump • O2 is final electron acceptor, no O2 = no echain Electron Transport Chain & ATP Synthase Electron Transport Chain • H+ ions flow back down gradient through ATP synthase • ATP synthase harnesses the proton motive force • ATP synthase adds a P to ADP to make ATP • Do you think the inner mito membrane is permeable to H+ ions? • This is the process of chemiosmosis Chemiosmosis Chemiosmosis • Chemiosmosis: an energy-coupling mechanism that uses energy stored in the form of an H+ gradient across a membrane to drive cellular work. • The e- chain and chemiosmosis together make up the process of oxidative phosphorylation – ATP is phosphoralayted – Oxygen is necessary • ATP/Glucose is 36-38, ATP Yield / Phase of Respiration Remember • Aerobic respiration uses oxygn A few alternatives • When O2 is not present Fermentation • Production of ATP w/o O2 • This is ANAerboic respiration • Glycolysis still in the picture – Rember O2 not needed for glycolysis – NAD+ is electron acceptor • Two common types… – Alcohol fermentation – Lactic acid fermentation Alcohol Fermentation • Pyruvate converted to ethanol, releasing CO2 • NADH is oxidized to make NAD+ Lactic Acid Fermentation • Pyruvate reduced by NADH • So did it gain or loose electrons? • Lactate is formed as waste product. Facultative Anerobes • Organisms that can do aerobic respiration when possible • Can switch to fermentation under aerobic conditions Glycolysis and Citric Acid Cycle • Intermediates of these processes can be diverted into a number of other anabolic pathways • Biosynthesis is the production of macromolecules • Many other compounds can be used to make ATP in cellular respiration – Other sugars – Proteins – fats Try these on for size… • Explain the specific role of glycolysis in cellular respiration. • Describe the function of water in cellular respiration and photosynthesis.