* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chemistry Of Life
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
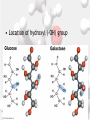
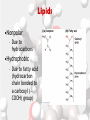
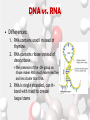
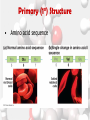
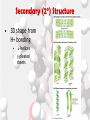
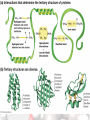
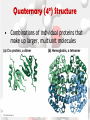
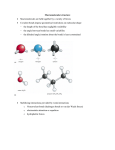
Chemistry Of Life: Carbon & Macromolecules Chapter 5 Carbohydrates • Structure: – Monosaccharides joined by glycosidic linkages to form polysaccharides • Function: – – – – Precursor to other molecules Structure Cell ID (glycoproteins) Energy storage Monosaccharide Structures vary due to… •Number of carbon atoms •Location of carbonyl (C=O) group • Location of hydroxyl (-OH) group • Linear and ring forms Polysaccharides • Polymerization – Condensation reaction between two hydroxyl groups called a glycosidic linkage. Types of Polysaccharides • -glucose polymer = For STORAGE • Starch (plants) – Glycogen (animals) • -glucose polymer = For STRUCTURE – Cellulose (plant cell walls) – Chitin (fungi cell walls, some algae, many animal exoskeletons) – Peptidoglycan (bacterial cell walls) To Release Energy • -Glycosidic Linkages Are Hydrolyzed by Enzymes to Release Glucose – Glycogen • Phosphorylase – Starch • Amylase •Glucose is then used to in the production of ATP Lipids •Nonpolar – Due to hydrocarbons •Hydrophobic – Due to fatty acid (hydrocarbon chain bonded to a carboxyl (— COOH) group) 3 Types of Lipids Found in Cells 1. Fats (Triglycerides) 3 Types of Lipids Found in Cells 2. Steroids Below: Cholesterol 3 Types of Lipids Found in Cells 3. Phospholipids • Amphipathic Selective Permeability of Lipid Bilayers Bond Saturation in the Hydrocarbon Chain • C=C can cause a “kink” – Prevent close packing of tails – reduce hydrophobic interactions • Unsaturated fats – Chains with at least one double bond • Saturated fats – No double bonds – More chemical energy Phospholipid Membrane Factors That INCREASE Membrane Permeability •More C=C •Shorter tail •Fewer cholesterol molecules in the membrane •Increased Temperature DNA •Store and transmit biological information, contained in the sequence of the bases. •Carries the information required for the growth and reproduction of all cells. •Stable, resistant to degradation. Nucleotides Polymerization DNA vs. RNA • Differences: 1. RNA contains uracil instead of thymine. 2. RNA contains ribose instead of deoxyribose. • The presence of the –OH group on ribose makes RNA much more reactive and less stable than DNA. 3. RNA is single stranded, can H+ bond with itself to create loops/stems Proteins • • • • • • • Structure Storage Transport Defense Catalysis Signaling Movement Primary o (1 ) • Amino acid sequence Structure Secondary • 3D shape from H+ bonding • -helices -pleated sheets o (2 ) Structure Tertiary o (3 ) Structure • Interactions between R-groups or between R-groups and the peptide backbone – – – – – H+ bonds hydrophobic interactions van der Waals interactions covalent disulfide bonds and ionic bonds Quaternary o (4 ) Structure • Combinations of individual proteins that make up larger, multiunit molecules Denaturation: Protein loses shape due to improper heat, pH, etc.