* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Lactate dehydrogenase wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Blood sugar level wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
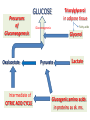
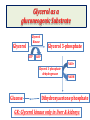
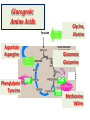
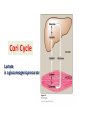
Introduction of Glucose Metabolism Lecture-4 GLUCONEOGENESIS GLUCONEOGENESIS Gluconeogenesis is the synthesis of glucose from glucogenic precursors which are not of carbohydrate origin (gluconeogenic precursors) It occurs during prolonged fasting to synthesize glucose for tissues requiring continuous supply of glucose as a source of energy: Brain, RBCs, Kidney medulla, Lens, Cornea, Testes, sk.ms Gluconeogenesis occurs ONLY in the liver & kidneys Gluconeogenic precursors 1- Intermediates of glycolysis by reverse of steps of glycolysis (except 4 steps that need 4 different enzymes) 2- Intermediates of citric acid cycle are converted to oxalacetate then to glucose 3- Lactate Lactic acid formed of anaerobic glycolysis in cells as RBCs & skeletal muscles are transported in blood to liver to be converted to pyruvate then to glucose (Cori cycle) 4- Glycerol Glycerol is derived from the lipid triacylglycerol in adipose tissue. Glycerol is convered into dihydroxyactone phosphate (intermediate of glycolysis) then to glucose. 5- Glucogenic amino acids of proteins Glucogenic amino acids are deaminated to form a-ketoacids a-keto acids are converted to pyruvate or intermediates of citric acid cycle then to glucose Precursors of Gluconeogenesis Oxalacetate Intermediate of CITRIC ACID CYCLE GLUCOSE Triacylglycerol in adipose tissue Fatty acids Gluconeogenesis Glycerol Pyruvate Lactate Glucogenic amino acids in proteins as sk. ms. Glycerol as a gluconeogenic Substrate Glycerol Glycerol Kinase ATP Glycerol 3-phosphate ADP NAD+ Glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase Glucose NADH Dihydroxyacetone phosphate GK: Glycerol kinase only in liver & kidneys Glucogenic Amino Acids Pyruvate Aspartate Aspargine Phenylalanin Tyrosine Amino acids Amino acids Glycine, Alanine Glutamate Glutamine Methionine Valine Cori Cycle Lactate is a gluconeogenic precursor Unique enzymes of gluconeogenesis Reactions 1, 2, 3 & 4 are catalyzed by enzymes NOT used in glycolysis GLUCOSE 1- Pyruvate to oxalacatate by pyruvate carboxylase 2- oxalacetate to phosphoenol pyruvate by PEP carboxykinase 3- Fructose 1,6 bisphosphate to fructose 6 phosphate by fructose 1,6 bisphosphatase 4- Glucose 6-phosphate to glucose by glucose 6-phosphatase Other reactions of gluconeogenesis are catalyzed by same enzymes of glycolysis in the reverse direction GLUCONEOGENESIS