* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Type three secretion system wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Lipopolysaccharide wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
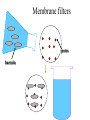
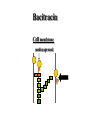
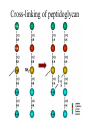
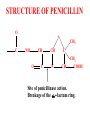
Key Words Sterilization/disinfection/antisepsis Bacitracin Antibiotic Vancomycin Selective toxicity beta lactam Bactericidal Penicillins Bacteriostatic Cephalosporins Minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) Monobactam Susceptibility testing Clavulinic acid Penicillin binding proteins Penicillinase/beta lactamase Autolysins Polymyxin B Cycloserine Resistance STERILIZATION • All killed • non-selective Sterilization • autoclaving – 121oC (heat/pressure) * Heat resistant materials • ethylene oxide – Non heat resistant – usually equipment • ultra-violet light – surfaces (e.g operating rooms) – not totally effective Membrane filters pores bacteria Disinfection • Liquids that kill bacteria – e.g. phenol based – too toxic for skin surfaces Antiseptics • Topical (e.g. skin) – e.g. iodine or 70% alcohol – “reduce” bacterial load ANTIBIOTICS • Selectively toxic for bacteria – bactericidal (killing) – bacteriostatic (growth inhibition) • no harm to patient Antibiotics • destroy structures – present in bacteria – not present in host Antibiotics work together with immune system Minimal inhibitory concentration • lowest level stopping growth • e. g. zone of inhibition around a disk impregnated with antibiotic • Antibiotics that inhibit cell wall biosynthesis are bactericidal • Without cell wall, osmotic pressure causes bacteria to burst Peptidoglycan synthesis Cytoplasm Cell Membrane undecaprenol sugar amino acid Cell wall Cycloserine 1. alanine (ala) analog 2. inhibits conversion of L-ala to D-ala 3. inhibits formation of D-ala-D-ala Cycloserine Analog of alanine Cytoplasm X X sugar amino acid X X Bacitracin • Inhibits dephosphorylation Bacitracin Cell membrane undecaprenol P P Vancomycin • binds to D-ala-D-ala • inhibits cross-linking Vancomycin Cell wall Beta lactam antibiotics • penicillins • cephalosporins • monobactams • inhibit penicillin binding proteins • stop cross-linking Beta lactams Cell wall Penicillin binding protein Cross-linking of peptidoglycan STRUCTURE OF PENICILLIN O S C NH CH O C CH N CH3 C CH CH3 COOH Site of penicillinase action. Breakage of the lactam ring. Attached to lactam ring • penicillins – 5 membered ring • cephalosporins – 6 membered ring • monobactams – no second ring Chemical modifications change biological activity • Early lactam antibiotics – inactive against Gram negative bacteria • no penetration of outer membrane Resistance mechansims • Produce beta lactamase (penicillinase) – destroys antibiotic • modified penicillin binding proteins – don’t bind antibiotic • modified porins – no internalization of antibiotic Clavulinic acid • beta lactam • binds strongly beta lactamases – inhibits activity Polymyxin B • binds – lipid A – phospholipids • disrupts outer membrane, Gram negative bacteria • toxic to human cells