* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download A2 Respiration test
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Gaseous signaling molecules wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
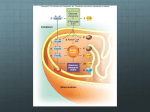
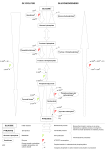
A2 Respiration test Total marks [40] The diagram below shows some of the stages in glycolysis: Glucose X Hexose phosphate X Hexose biphosphate Triose phosphate Y Pyruvate Z Reduced Z in the cytoplasm State precisely where this process occurs ………………………………………[1] ATP/phosphate group from ATP Identify substance X ……………………………………………..…………………[1] hydrogen Identify substance Y ………………………………………………………………..[1] Briefly outline the fate of substance ‘reduced Z’ ………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………….. …… Enters mitochondria; is (re-)oxidised; in the electron transport chain; ………………………………………………………………………………………..[2] Carefully read the following account of aerobic respiration and then fill in the blanks: cytoplasm In the first stages of respiration which occurs in the ……………………………………….. of the cell, glucose is ……………………………….. to pyruvic acid. Glycolysis yields …………………………. oxidised ATP and a reduced coenzyme. acetyl CoA The pyruvic acid then combines with coenzyme A to form …………………………………….. which enters the Kreb’s cycle which occurs in the …………………………………………. of the matrix ……………………………………………….. mitochondria During these reactions hydrogen atoms are removed from a series of intermediate compounds by enzymes called …………………………………… dehydrogenases . The hydrogen atoms are passed to carriers such as ……………………………………… . NAD/FAD oxidised In the third stage of aerobic respiration, the carriers are alternately reduced and ……………………. electrons as they gain and lose …………………………. . Energy is released and used to phosphorylate ADP, forming ………………………. . The hydrogen atoms finally combine with……………………….. to form ATP oxygen ……………………………. . water [13] Below is a diagram of a mitochondrion a) Add labels where indicated. [5] matrix cristae b) any point on the inner membrane outer membrane inner membrane intermembrane space b) Indicate on the diagram the precise site of the electron transport chain [1] An experiment was carried out to measure the rate at which a sample of mitochondria used oxygen under different conditions. The mitochondria were placed in a well oxygenated liquid with a water potential equal to the water potential of their contents. At time A, an end-product of glycolysis was added to the liquid. At times B, C and D, ADP was added. The same amount of ADP was added each time. The results of this experiment are shown in the graph below: Oxygen concentration in the liquid A B C D 0 2 4 Time (mins) 6 8 a) Explain why the liquid used in the experiment should have the same water potential as the contents of the mitochondria ………………………………………………………………… • to ensure there is no net movement of water/osmosis ………………………………………………………………… • that would cause a dilution/concentration of the matrix contents ………………………………………………………………… • or damage to mitochondria/bursting of organelle ………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………… [2] b) (i) State the name of the substance that was added at A pyruvate/pyruvic acid ……………………………………………………………… [1] (ii) Name the two stages of the respiratory process that take place in the mitochondria …………………………………………………………… link reaction; Kreb’s cycle; ETC; oxidative phosphorylation …………………………………………………………. [2] (iii) State the role of oxygen in these respiratory processes ……………………………………………………………… to reoxidise the last substance/last cytochrome in the ETC ……………………………………………………..………. [1] c) Explain the result of adding ADP at the following points on the graph; (i) B and C …………………………………………………………………………… • oxidative phosphorylation can occur/ADP converted to ATP • which requires oxygen …………………………………………………………………………… • to react with hydrogen to form water • less occurs at C than B because amount of reduced coenzymes is less/ORA …………………………………………………………………………… Oxygen concentration in the liquid ………………………………………………………………………..… [3] A B C D 0 2 4 Time (mins) 6 8 (ii) D .............................................................................................................. • no reaction occurs • due to lack of reduced NAD/FAD • which means lack of hydrogen ions/electrons for ETC ……………………………………………………………………..……… [2] B Oxygen concentration in the liquid A C D 0 2 4 Time (mins) 6 8 Yeast cells can respire anaerobically using glucose as a substrate. (i) State the end products formed from the glucose if oxygen is not available to the yeast cells • ethanol/ethanal ……………………………………………………………………………………………… • carbon dioxide ……………………………………………………………………………………………… [2] (ii) Explain why ADP is required in anaerobic conditions • ……………………………………………………………………………………………… to form ATP • ……………………………………………………………………………………………… because glycolysis occurs • that requires additional ADP • ……………………………………………………………………………………………… to give a net gain of 2 ATP molecules ……………………………………………………………………………………………… [3]