* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Hallucinogens - People Server at UNCW
Discovery and development of angiotensin receptor blockers wikipedia , lookup
Cannabinoid receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
NK1 receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Toxicodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
NMDA receptor wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinic agonist wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Non-specific effect of vaccines wikipedia , lookup
Psychedelic therapy wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Theralizumab wikipedia , lookup
5-HT3 antagonist wikipedia , lookup
5-HT2C receptor agonist wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Dydrogesterone wikipedia , lookup
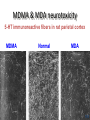
Methylated AmphetaminesMDA and MDMA • Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA, Ecstasy, XTC)-MDA is a metabolite of MDMA and may be responsible for much of the MDMA effect. • Synthesized in 1912 • Structurally related to amphetamines – – – – Sympathomimetic Weak in altering perceptual functions But strong effects on emotions - empathogen Used in combo with psychotherapy Of interest: http://www.biopsychiatry.com/interview/index.html Ecstasy (MDMA): Physiological Effects • Sympathomimetic • Bruxism & Trismus—teeth grinding & jaw clenching (pacifiers) • Dehydration/Overhydration • Hyperthermia • Tachycardia Ecstasy (MDMA): Psychological Effects • Increased alertness, arousal, insomnia-stimulant effects • Euphoria, increased emotional warmth • Increased empathy and insight? • Hallucinogenic effects are largely absent Percent Using Percent School Seniors Seniors reporting Percent HighHigh School reporting use during their Senior year MDMAMDMA use during their Senior year (Johnston, O'Malley,Bachman (Johnston, O'Malley,Bachman & Schulenberg, 2005) & Schulenberg, 2005) 8 6 4 2 98 96 96 98 00 Year 02 00 04 06 History • Patented by Merck in 1914 • Advocated by some as adjunct to psychotherapy (1970s-80s) • A “Designer Drug”…Picked up the name “ecstasy” & became significant street drug (1980s) • Schedule I drug (1986- The Analogue drug Act) • Prototype “club drug” (1990s) MDMA: Prototype Club Drug Pharmacodynamics Monoamine neurotransmission – increase synaptic DA and 5-HT – blocks 5-HT transporter – enters neuron and causes release of 5-HT Ecstasy and brain Damage?: Preclinical research • Serotonin depletion, damage to serotonergic neurons reported in several species including rats and primates (see Morton, 2005 for a review) • Effects were present in primate brain 7 years after MDMA exposure Hatzidimitrious et al., 1999) MDMA & MDA neurotoxicity 5-HT immunoreactive fibers in rat parietal cortex MDMA Normal MDA 9.9 Are doses used in preclinical research too high? • neurotoxic doses in non-humans (5-20 mg/kg twice or more/day for several days) are generally higher than would be typical of human use. • However, people often take several tablets at a time or throughout a night’s binge and a tablet may contain up to 300 mg: 4-5 mg/kg in an average person. X Toxicity • Malignant hyperthermia and dehydration • Idiopathic toxic response (not common but nasty) – Renal failure – Rhabdomyolysis – disintegration of muscle tissue • seizures, arrhythmias, heart failure, stroke, • Most MDMA-related fatalities have been attributed to symptoms of heat stroke and hyperthermia Residual (long-term) adverse effects? • Topp et al. (1999) Australia study • Physical side effects – Loss of energy (65%), Muscular aches (60%) – Hot/cold flashes (48%), Numbness (47%) – Profuse sweating (43%), Tremors (42%) • Psychological side effects – – – – – Depression (56%), rritability (63%), Sleep difficulty (56%), Confusion (47%) Anxiety (45%), Paranoia (40%) Memory deficits? ( note issue of sample problems/poly-drug use etc..) What is PMA? • Paramethoxy-amphetamine • "Death" "Mitsubishi Double Stack" "Killer" "Red Mitsubishi" • Substitute for MDMA • Cheaper to make • Slower, longer effects • More hallucinogenic • Incidence of toxic side effects much higher than MDMA (narrow safety margin) Myristin and Elemicin • • • • Found in nutmeg and mace Structurally similar to mescaline Significant nausea and vomiting The sickness usually limits use Glutamatergic Psychedelics AKA-Dissociative Anesthetics: -Phencyclidine (PCP, Angel dust, Lovely) -Ketamine (Special K) Phencyclidine PCP Glutamate (NMDA) receptor antagonist Blocks the function of glutamate Used as an analgesic and anesthetic Can be administered by any route Oddly enough, animals self-administer (euphoria) PCP- physiological effects • numbness, loss of motor coordination, slurred speech, blurred vision, Nystagmus Higher doses lead to: hyper excitability or stupor coma seizures death A perfect example of a Schedule I drug • High rate of psychotic episodes some long-term Subjective Effects of PCP/Ketamine • Sensations of light coming through the body and/or colorful visions • Complete loss of time sense • Bizarre distortions of body shape or size • Altered perception of body consistency • Sensations of floating or hovering in space • Feelings of leaving one’s body • Visions of spiritual or supernatural beings • Emotions ranging from euphoria to hositlity true psychosis Hallucinations, paranoia, agitation, dissociation Dalgarno & Shewan (1996) Ketamine • Special K • Very similar to PCP, not as powerful • Liquid, but can be powdered for snorting or smoking • Another perfect example of a Schedule I drug Dextromethorphan • • • • • Active ingredient in most OTC cough medicine NMDA receptor blockade at high doses Mostly teenage males abuse it Like PCP and K at 20-30 X OTC dose Coricidin –Bad news Cholinergic Hallucinogens Anticholinergic hallucinogens • Atropine-Deadly nightshade, Datura, Jimson weed, and Mandrake, Atropa belladonna • Scopolamine-from Datura, Jimson weed, Mandrake and Henbane Cholinergic Hallucinogens Acetylcholine receptor (muscarinic) antagonists Dissociatives that induces delirium , hallucinations, and amnesia Classic anti-cholinergic symptoms Hot as hell Dry as a bone Mad as a hatter Blind as a bat Red as a beet Used in the treatment of motion sickness & to dilate pupils during eye-exams. Datura Jimson weed Anticholinergic effects • Dry mouth, blurred vision, loss of motor control • Dream-like trance state • Little or no memory of experience Muscarine/Muscimol Found in mushrooms (Amanita Muscaria) Muscimol is a GABAA agonist Trance-like, dreamy state with dreamlike illusions Like Ambien Muscarine is an Acetylcholine agonist (muscarinic receptors) Not psychotropic Peripheral effects: sweating, limb twitching, seizure activity Salvia Divinorum • Plant used by the Mazatec people of Southern Mexico: Diviner’s sage—leaves chewed or smoked • Active substance = salvinorum A (affects Kappa receptors)--most potent natural hallucinogen (100 microgram ED50) Salvia Divinorum Brief (30-60 min) intense trip: visual hallucinations, dissociative state, some bad trips, recent highly publicized suicide Marketed legally in US (in most states) as herbal dietary supplement—currently under DEA review