* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download (2-aminoethyl) imidazole
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of proton pump inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
5-HT2C receptor agonist wikipedia , lookup
Toxicodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinic agonist wikipedia , lookup
CCR5 receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of beta-blockers wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of TRPV1 antagonists wikipedia , lookup
NMDA receptor wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of antiandrogens wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
5-HT3 antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of angiotensin receptor blockers wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Cannabinoid receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
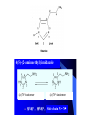
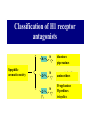
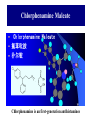
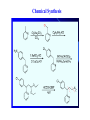
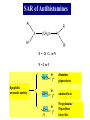
Chapter 3.4 Antihistamines Histamine H1 Antagonists The term antihistamine historically refers to drugs that antagonize the actions of histamine at H1 receptors. Histamine is an important chemical mediator of hypersensitivity 4 (5-)-(2-aminoethyl)imidazole H N N CH 2CH 2NH2 Ethylamine Imidazole 4(5)-(2-aminoethyl) imidazole (a) N-tautomer (a) N-tautomer Side chain N = N Properties and Action of Histamine +NH3 H N N At pH 7.4, histamine exists almost exclusively (96.6%) in a monocationic form Most histamine is synthesized and stored in mast cells and basophilic granulocytes Histamine is mediated by specific cell surface receptors (H1, H2, and H3) NH2 HN N COOH ×é°±Ëá histidine histidine decarboxylase ×é°±ËáÍÑôÈø NH2 HN Biosynthesis and metabolism of histamine SAM SAH N ×é°· histamine N-methyl N-甲基转移酶 transferase MAO (brain) 单胺氧化酶-B (´ó ÄÔ) DAO (peripheral) ¶þ°· Ñõ»¯Ã¸dehydorgenase (Íâ ÖÜ) Aldehyde È©ÍÑÇâø NH2 H3C N COOH N HN N imidazolyl acetic ßäßòÒÒ Ëá acid N-¼×»ù×é°· N-methyl histamine ribose phosphate 磷酸核糖转移酶 MAO (brain)(´ó ÄÔ) 单胺氧化酶-B DAO (peripheral) ¶þ°· Ñõ»¯Ã¸ (Íâ ÖÜ) Aldehyde È© ÍÑÇâø dehydorgenase transferase COOH COOH H3C N O HO N N N N-methylimidazolyl N-¼×»ùßäßòÒÒ Ëá acetic acid HO OH Imidazolyl acetic acid ßäßòÒÒ ËáºËÜÕ necleoside Classification of H1 receptor antagonists N lipophilic 亲脂性芳环部分 aromatic moiety O C N N N diamines 乙二胺类,哌嗪类 piperazines 氨基醚类 aminoethers Propylamine 丙胺类、哌啶类、三环类 Piperdines tricyclics Histamine H1 Receptor Antagonists – – – – – – – ethyl diamines aminoethers propylamines:chlorphenamine maleate tricyclics:loratadine piperazines:cetirizine hydrochloride piperidines:mizolastine others Ethyl diamines H1 receptor antagonists • Ar = Ph、p-subPh or thtiophenyl;Ar’= Ph or 2pyridinyl,R and R’ = Me or heterocyclyl。 Ar Ar' N N • Weaker action to H1 receptor,moderate central analgesic effect,causing disorder of gastrointestine, local external use may cause skin hypersensity. Aminoethers H1 receptor antagonists • If Ar(Ar)CHO- replace ArCH2(Ar’)N- moiety in ethyl diamines, then you get aminoethers. Ar' Ar O R' N R • The first generation of H1 receptor antagonist display apparent analgesic and anticholinergic effects,usually with side reaction like somnolence, dizzy, oral dryness. But incidence rate of gastrointestine reaction is low. Some of drugs could be applied in the treatment of insomnia. • For those aminoether with two aromatic group,the activity of Sisomer is usually higher than that of R-isomer. Aminoethers H1 receptor antagonists Antihistamine drugs without analgesic effect belonged to aminoether type,they have higher selectivity to peripheral H1 receptor, belong to second generation antihistamine drug. Cl O O N Cl Clemastine Setastine N Propylamines H1 receptor antagonists • When ArCH2(Ar)N- in ethyldiamines is replaced by Ar(Ar)CH- moiety,or omitted -O- in aminoether, then propylamine is there. R' Ar N R Ar' • Compared to traditional antihistamines like ethyldiamines, aminoethers, tricyclics,propylamines have stronger antihistamine action but weaker central analgesic, and less tendency of inducing somnolence. Chlorphenamine Maleate Chlorphenamine is an first-generation antihistamines Action of Chlorphenamine Maleate Cl O N . OH OH N O • Stronger antihistamine action,less dosage,less side effect,suitable for children. Mainly use for hypersensitive nasitis, skin mucosa hypersensitivity, urticaria, angiectatic nasitis, hay fever,contact dermatitis and hypersensitivity caused by food and drugs. Side effect: somnolence, thirsty, diuresis. Points Need Your Concerns Cl N H N S(+) -Chlorphenamine • One chiral center in Chlorphenamine,there is a pair of optical isomer. The activity of S-isomer is twice stronger than that of racemate,acute toxicity is also less. The activity of R-isomer is only 1/90 than that of racemate。In clinic, racemate chlorphenamine maleate is used。 Chemical Synthesis Propylamines H1 receptor antagonists N H N COOH Acrivastine • Allyl acid make the compound more hydrophilic and it is more difficult for it to enter into central nerve system.Therefore, acrivastine displays no analgesic effect. • The activity of E-isomer is great higher than that of Z-isomer. Tricyclics H1 receptor antagonists • If fused together the adjacent position of two aromatic ring, tricyclics H1 receptor antagonist is there. Y X N R R' • If X = N,Y = S,then phenothiazine • If X= C (sp2),Y is replaced with bioisostere, -CH=CH-,then cyproheptadine • Further modification of cyproheptadine produce loratadine Loratadine Cl N N O O • Strong selective H1 receptor antagonist, but no anticholinergic activity and central nerve system inhibition, belong to second generation non-sedative antihistamines. • The main difference compared to other tricyclics antihistamines, is the replacement of neutral aminoformate for basic tertiary amine. It is believed this is the reason of its decrease of central analgesic . Chemical Synthesis of Loratadine N CN H2SO4 Cl 1) n-BuLi/NaBr, THF t-BuOH O N Cl 2) Cl POCl3 O N NHBu-t NHBu-t Cl Cl N 1) ClMg N Cl O N PPA N 2) HCl CN N N ClCOOC2H5 PPA, P2O5 Cl O Cl N COOC2H5 N N O Zn, TiCl4 N O O Piperazines H1 Receptor Antagonists • When Ar(Ar)CHN- replaces ArCH2(Ar)N- moiety in ethyldiamine, and make two nitrogen atom in piperazine ring, then the piperazines antihistamines are constructed Ar' Ar N N R • Other than stronger H1 receptor antagonism effect,they display other characteristic,like relieving asthma effect, antikinetia action, and blocking action of Ca2+ ion channel . Cetirizine Hydrochloride O Cl N N O OH .2HCl • Because of the easy ionization of Cetirizine, the drug is not easy to permeate blood brain barrier (BBB) , little amount of the drug is able to arrive central nerve system, it belongs to non-sedative antihistamine, it is one of the representative drug of second generation antihistamines. The advantages of Zyrtec is that 1. Once-daily dosing 2. Rapid onset of activity (20-60 min) 3. Minimal CNS effects Process for Synthesizing Cetirizine Hydrochloride Cl Cl NH Cl(CH2)2OCH2CN K2CO3 N N O Cl 1.KOH 2.HCl N O N OH N 2HCl O N Piperidines H1 Receptor Antagonists • Limitation of the entrance to central and increase the selectivity to H1 receptor, is the guiding ideology for design and searchin new antihistamine drugs. This resulted in the development of non-sedative H1 receptor antagonists. • Clemastine(aminoethers)、Acrivastine(propylamines)、 Loratadine(tricyclics), and Cetirizine(piperazines)all belong to non-sedative H1-receptor antihistamines. Via the introduction of hydrophilic group, the drug is difficult to enter central nerve system because of BBB, therefore the sedative effect is overcome (weakened). Whilst Clemastine and Loratadine have higher selectivity to peripheral H1 receptor, therefore avoid side effect to Centrum. Other non-sedative antihistamine drugs belong to piperidines selective peripheral H1-receptor antagonists. Mizolastine F N N N N N HN O • 2-[[1-[1-[(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]-1H-benzimidazol-2yl]-4-piperidinyl]methylamino]-4(1H)-pyrimidinone • 2-〔〔1-〔1-〔(4-氟苯基)甲基〕-1H-苯并咪唑-2基〕哌啶基-4-基〕甲基氨基〕嘧啶-4(3H)-酮 Process for Synthesizing Mizolastine F HN N Cl H N N NaH F HBr N H N N O O H N F N N NaOCH3 N HN O O N K2CO3 F H N S N F CH3I N O N N O N N HN O N N N N HN O SAR of Antihistamines Ar R X (CH2)n N Ar' R' X = O, C, or N N = 2 or 3 N lipophilic 亲脂性芳环部分 aromatic moiety O C N N N diamines 乙二胺类,哌嗪类 piperazines 氨基醚类 aminoethers Propylamine 丙胺类、哌啶类、三环类 Piperdines tricyclics