* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Dr Richard Stevenson
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Polysubstance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of beta-blockers wikipedia , lookup
Cannabinoid receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of angiotensin receptor blockers wikipedia , lookup
Environmental impact of pharmaceuticals and personal care products wikipedia , lookup
5-HT2C receptor agonist wikipedia , lookup
5-HT3 antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Toxicodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Theralizumab wikipedia , lookup
NK1 receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Environmental persistent pharmaceutical pollutant wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Dydrogesterone wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
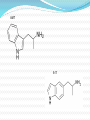
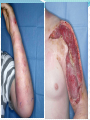
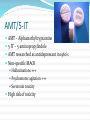
Clinical Experience of Novel Psychoactive Substances Dr Richard Stevenson Background Legal Highs -> Novel Psychoactive Substances 41 new substances in 2010 alone Diverse collection of compounds Piperazines Cathinones Synthetic cannabinoids Isolated compounds Recreational problem identified in 2008/2009 Varying legal status GRI Emergency Dept Experience 12 AMT 22 synthetic cannabinoids 3 cathinone 2 methoxetamine 1 salvia 9 life threatening toxicities Why are people taking them? Legal status Perception of safety Difficult to detect Point of care urine testing Odourless Availability Internet “Head shops” Sold as other drugs AMT 5-IT Common Problems Lack of reliable data “Not what is says on the tin” Dosage Inter-individual variability Time of onset to effect Polysubstance misuse Interactions ? Challenges in Clinical Care Acute Identification of xenobiotic Lack of toxicological data Mechanism of action Duration Clinical effects Appropriate treatment Chronic Long term psychological effects Long term physical effects Cathinones Synthetic variations of natural cathinones in Khat Mephedrone, methedrone, naphyrone Ivory wave, meow-meow, bubbles, ocean snow, NRG Sympathetic Toxidrome ↑HR, RR, BP, temp Tremor, agitation, paranoia, hallucinations, seizures ***duration 24 – 48 hours*** Treatments Benzodiazepines +/- haloperidol Piperazines Developed in 1950s – anti-helminthic agents BZP “Benzo Fury” Neurotransmitter release/reuptake inhibition Phenylpiperazines Direct serotonin receptor activation Reversal of serotonin uptake Clinically Sympathetic toxidrome Serotonin toxicity? Synthetic Cannabinoids Annihilation, Black Mamba, Spice, K2 Structurally dissimilar to THC Herbal material sprayed with chemicals Clinical effects Nausea +++ Collapse Some psychotropic effects Methoextamine Structurally similar to ketamine NMDA receptor agonist Clinically (dose related) Excitation, tachycardia, euphoria Hallucinations Dissociation Prolonged neurological effects - ataxia Supportive management AMT/5-IT AMT – Alphamethyltryptamine 5-IT – 5-aminopropylindole AMT researched as antidepressant in 1960’s Non-specific MAOI Hallucinations +++ Psychomotor agitation +++ Serotonin toxicity High risk of toxicity Serotonin Toxicity Exposure to a serotonergic drug Clinical features Confusion Autonomic instability Hyperkinetic musculoskeletal system Treatment of Serotonin Toxcity Morbidity & Mortality related to hyperthermia Temp ≥40 oC Duration Consequences Rhabdomyolysis Acute kidney injury Acidosis Cerebral damage Treatment of Serotonin Toxicity Aggressive cooling Antipyretics do not work! Control muscular activity High dose benzodiazepines Haloperidol for severe non-responders Appropriate fluid control BP control agents Anaesthesia with muscle paralysis The Future? Market flooded with NPS Difficult to legislate/control Long term effects?