* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 1
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
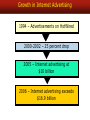
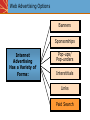
The Internet and Interactive Media Why the rapid adoption of the Internet? Growth in Internet Advertising 1994 – Advertisements on HotWired 2000-2002 – 25 percent drop 2005 – Internet advertising at $10 billion 2006 – Internet advertising exceeds $16.9 billion Internet Communications Objectives Create Awareness Answer Questions Create Buzz Stimulate Trial Generate Interest Objectives Create a Strong Brand Disseminate Information Create an Image Levels of Internet/Web Engagement • Placeholder • Business brochure (online collateral) • Image Development Vehicle • Public Relations Tool • Community / Network for Consumers • E-Commerce Site • Sales Promotion Tool • Product Review Source (ok to disparage products you sell?) • Source for Detailed Product Information and Links to Peripheral Sites/Information of Interest Huggies Provides Information & Community for Expecting Mothers Design Effectiveness - The Web Site Web Design Effectiveness Principles & Practices • Repeat yourself often. Then repeat yourself more. • Layer your information. Layered information is a key unique advantage of web advertising. • Text is STILL better than graphics! • Make as much immediately visible as possible without scrolling or linking. • Home pages are portals and matchmakers – not deep selling devices or closers. (Think pre-approach-approach-…close sale, AIDA, etc.) • White space - good, clutter - bad, but consider placing the optimal number of teasers with hot-links as white space will allow. • Remember the “3-click Rule”: Get users there in three clicks or less, or else…! • Hire a development firm that has technical/programming, design/aesthetic AND marketing sensibilities. • Produce final edited text before giving to developer. • Small text, width and central screen position is best for most browsers. • Division of Labor: Design and Layout, Content, Technology – who’s responsible for what? • Double the amount of time estimated to complete your website. Web Advertising Options Banners Sponsorships Internet Advertising Has a Variety of Forms: Pop-ups/ Pop-unders Interstitials Push Links Technologies Paid Search Typical Banner Ads Sales Promotions Are Common on Websites Public Relations on the Internet Internet Measures of Effectiveness Visit Measures Hits – # times a site is visited Unique Visitors - # of different viewers per time period Referrals In, Referrals Out Transaction/ROI Measures Click-through % – The internet equivalent of “response rate” Conversion %: The % of those clicking-through who transact Cost Per Conversion/Burn Rate - $ spent to convert prospect into transacting customer Frequency to Conversion Ratios: Measures effective frequency Action - Sales, Inquiries, etc. Navigation Measures Average Page Views - # of pages viewed (duplicated & unduplicated) Average Page Depth – How many pages are viewed per visit, on average Average Visit Time – How long the user stayed Other Measures/Methods Eye-Tracking: Captures physical eye movements Cross-Media Lift: Measures synergies between internet ads and other media Traditional Advertising Measures – Recall, Recognition, Brand Preference, etc. Internet Advantages and Disadvantages Advantages Disadvantages High Targetability & Target Marketing Involvement Demographics Measurement Measurement problems Problems Message/Offer Tailoring – Ad Message Tailoring Serving Capability Annoyance Interactive Capabilities Clutter Layered Information Access Information Access Potential for deception Commerce Sales Potential Potential Privacy Availability Creativity & Self-pacing Poor reach Exposure/Speed Flexibility Site Stability Complement to IMC