* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Alkene/Alkyne Addition Reactions
Enantioselective synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fischer–Tropsch process wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic resolution wikipedia , lookup
Cracking (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
1,3-Dipolar cycloaddition wikipedia , lookup
Wolff rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Aromatization wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Ene reaction wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
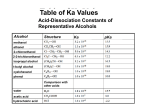
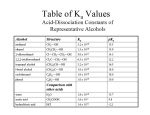
Alkene/Alkyne Addition Reactions The double and triple bonds present in alkenes and alkynes, respectively, make them much more reactive than alkanes. Alkenes and alkynes undergo addition reactions a reaction in which parts of a reactant are added to the two atoms that make up a double or triple bond Alkene/Alkyne Addition Reactions Two simple addition reactions: H H C=C H H H + Br2 H H-C-C-H Br Br Cl Cl H-C C - H + 2 Cl2 H-C-C-H Cl Cl Alkene/Alkyne Addition Reactions Some of the common reactants that can add to alkenes and alkynes include: Br2 I2 Cl2 H2 (requires a transition metal catalyst) H2O (requires a strong acid catalyst) HBr HCl HI Alkene/Alkyne Addition Reactions Example: Write the structure of the product that forms when 1-butene reacts with the following reagents (individually): Br2 H2 + Ni catalyst HBr Alkene/Alkyne Addition Reactions Markovnikov’s Rule: The major product obtained from the addition of an unsymmetrical reagent such as H-Br, H-Cl, or H-OH to an alkene or alkyne is the one obtained when the H atom of the reagent is added to the C atom of the multiple bond that already has the greater number of H atoms. “The rich get richer” Alkene/Alkyne Addition Reactions Example: Write the structure of the product that forms when 1-propyne reacts with the following reagents (individually): Br2 (excess) H2 (excess) with Ni catalyst HBr (excess) Alcohols Alcohols: hydrocarbon derivatives in which one or more of the H atoms has been replaced by a hydroxyl group (alcohol functional group) C-O-H OR C - OH Hydroxyl groups Alcohols Alcohols are named in the exact same manner as alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes except: To find the base name, drop the “e” from the name of the corresponding alkane and add “ol” Use the carbon number to identify the position of the alcohol. CH3CH2CHCH3 CH3CH2CH2OH 1-propanol OH 2-butanol Alcohols Examples: Draw the structures for the following alcohols. Methanol Ethanol 2-Propanol 2-methyl-2-propanol Alcohols The position of the alcohol in the chain has a significant impact on the reactivity of the alcohol. A primary alcohol (1o) is an alcohol in which the OH group is attached to a carbon which is bonded to only 1 other C atom. CH3CH2OH Alcohols A secondary alcohol (2o) is an alcohol in which the OH group is attached to a carbon which is bonded to two other carbon atoms. CH3CHCH3 OH CH3CH2CHCH2CH3 OH Alcohols A tertiary alcohol (3o) is an alcohol in which the OH group is attached to a C which is bonded to three other carbon atoms. CH3 CH3CCH3 OH CH2CH3 CH3CH2CCH3 OH Alcohols Example: Identify the following alcohols as 1o, 2o, or 3o. Name each alcohol. CH3 CH3CHCH2OH CH3 CH3CH2CCH3 OH CH3CHCH2OH OH Reactions of Carboxylic Acids Carboxylic acids contain a carboxyl group: O CH3C-O-H OR CH3CO2H Carboxyl group Reactions of Carboxylic Acids Carboxylic acids can participate in a variety of reactions: acid-base reactions similar to those of inorganic (without CC bonds) acids condensation reactions esterification amidation Reactions of Carboxylic Acids Esterification: a condensation reaction in which a carboxylic acid reacts with an alcohol to form an ester and water. O CH3C - OH + HO-CH2CH3 O CH3C-O-CH2CH3 + H2O Reactions of Carboxylic Acids Example: Predict the products formed during the following reactions. O CH3C - OH + CH3 CH2CH2OH O C - OH + CH3OH Reactions of Carboxylic Acids Amidation: a condensation reaction in which a carboxylic acid reacts with an amine that contains a hydrogen bonded to nitrogen to form an amide and water O O CH3C - OH + H2N-CH2CH3 CH3C-NH-CH2CH3 + H2O Reactions of Carboxylic Acids Example: Predict the products formed during the following reactions. O CH3 CH2C - OH + CH3CH2NH2 O C - OH + CH3NH2