* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download No Slide Title
Homology modeling wikipedia , lookup
Protein domain wikipedia , lookup
Protein folding wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Bimolecular fluorescence complementation wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
Protein mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
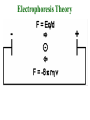
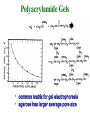
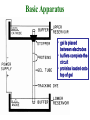
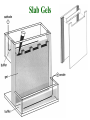
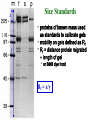
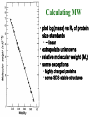
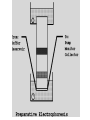
Electrophoresis Theory electric field strength mobility net charge size v = (E/d)(q)/(6r) shape viscosity (applied voltage)(net charge) mobility = (frictional coefficient) Gel Electrophoresis • friction is ease at which molecule passes through pores • size is the major determinant (voltage)(charge) mobility = (frictional coefficient) mobility (voltage)(charge/mass) Polyacrylamide Gels • common matrix for gel electrophoresis • agarose has larger average pore size Basic Apparatus • gel is placed between electrodes • buffers complete the circuit • proteins loaded onto top of gel Slab Gels Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (SDS) • strongly denaturing detergent • disrupts 2o, 3o, and 4o structures • binds and confers negative charge to protein • charge is proportional to mass SDS-PAGE • proteins are unfolded (ie, random coil) • ~ uniform charge/mass ratio due to SDS • therefore endogenous charge and shape are not major factors • mobility is inverse of mass (charge) mobility (voltage) (mass) Size Standards x y • proteins of known mass used as standards to calibrate gels • mobility on gels defined as Rf • Rf = distance protein migrated length of gel • or BB dye front Rf = x/y Calculating MW • plot log(mass) vs Rf of protein size standards • ~ linear • extrapolate unknowns • relative molecular weight (Mr) • some exceptions • highly charged proteins • some SDS-stable structures Practical Considerations • prepare gels • choose % acrylamide • prepare samples • stacking gel buffer + 2% SDS • b-mercaptoethanol • heating (37o boil) • electrophoresis • amount of sample • voltage • tracking dye (BB) • detect proteins • eg, Coomassie blue % acrylamide • protein size range • gradient gels • desired resolution • amount of sample Voltage • voltage = time, but heat • resistance during electrophoresis (E=IR) Preparative Electrophoresis • high resolution provides analytical information • difficult to exploit in protein purification • recovery of proteins from gels • diffusion • electroelution • transfer to membrane • immunization • limited protein capacity • special apparatus