* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified organism containment and escape wikipedia , lookup
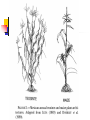
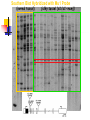
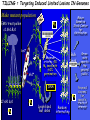
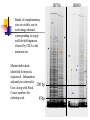
USEFUL MUTANTS Heritable changes can result in a useful novel phenotype, i.e., a new allele. Other Kinds Some “not bad” Mutants Sweet Corn Single gene mutations in several different starch biosynthesis genes have been introduced into tender, flavorful corn to produce the sweet corn we eat today Instead of transferring sugars into starch, they accumulate ‘sweetness’. Shrunken (Supersweet), sugary, sugary enhancer, amylose extender. Ornamental Corn Single gene mutations in the anthocyanin (pigment) production pathway lead to the colored kernels we see on an ear of Indian corn. Waxy Corn A mutation in the waxy gene is used in production of tapioca and other gelling starch products. High-lysine Corn A mutation in the opaque2 gene results in increased levels of the essential amino acid, lysine. Quality Protein Maize (QPM). o2, opaque endosperm: endosperm soft and opaque; high lysine content; regulates b-32 protein. Photo: seed from a selfed ear segregating for opaque kernels in transmitted light showing opaqueness of mutant kernels. And of course - Disease resistance Insect resistance Glossy mutants Flowering time Cytoplasmic male sterility Nutritional changes “Value-added” changes Mutations and Co-evolution Variations usually exist in nature. Co-existing species experience mutual selection. Domestication by Culture Suppression of ‘Wild’ Traits Seed scattering Mixed timing Hard-shelled seeds Mutation/Selection of ‘Desired’ Traits Packaging Convenience Storability Processing Domestication in Wheat DIVERGENCE, CROSSING, SELECTION Earliest cultivated and wild wheat, with the 7chromosome A genome (left), crossed with another, with the B genome, (third) about 8000 BC. The result was durum wheat (emmer = PASTA WHEAT), fourth in this photo. Emmer crossed with wild goat grass (fifth) and gave rise to the staff of life (BREAD WHEAT), sixth. The combination, AABBDD, 7x3 = 21 chromosomes, is productive and high in food quality. Dwarf Wheat Opened Doors Ninetieth birthday of the Father of the Green Revolution, Nobel Peace Prize Laureate Norman Borlaug http://www.cimmyt.org/english/webp/support/news/borlaug_90.htm New Wheats a la Nature Deliberate employment of diversity in collections. Crosses of AABB with diverse DD and others. Mutant Images for Maize http://www.maizegdb.org/cgi- bin/imagebrowser_phenotypes.cgi Ramosa tassel and ear Terminal ear1 Teopod2, Tunicate1 White pollen1 (bursting) Virescent1 Directed Transposon Tagging An example---cloning the male sterile silky1 (si1) gene using Mutator. si1 y1/si1 y1 X Si1 Y1/Si1 Y1, Mu-active (white seed/silky tassel) X (Yellow seed/normal tassel) all Yellow seed (y1/Y1) si1 y1/Si1 Y1 (99.99%) Normal Phenotype si1 y1/si1-mum Y1 (rare mutant 1/10000) X Si1 y1/Si1 y1 Yellow seed have tagged si1 allele (Si1 y1/si1-mum Y1) Grow plants from yellow seed and backcross to si1 y1/si1 y1. Plant out seeds, score for silky vs normal tassel phenotype. Prepare DNA from leaves of each type. Perform co-segregation analysis to identify transposon linked to your mutant phenotype. Southern Blot Hybridized with Mu1 Probe (normal tassel) (silky tassel (si1/si1-mum)) TILLING = Targeting Induced Limited Lesions IN Genomes Make mutant population EMS treat pollen c1 Sh1 Bz1 Maize Genetics Stock Center for distribution M2 bz1* sh1* Minimum criteria: ≥50 M2 seed with ≥60% germination Bulk Seed DNA C1 sh1 bz1 M0 M1 M3 Lyophilized leaf disks Random intermating Growouts open to the general public Forward screens for specific traits of interest DNA prepared and equal amounts of each sample arrayed to microtiter wells, then these 8-fold pooled IR-labeled primers create double end-labeled fragments IR700 Bands of complementary size are visible, one in each image channel, corresponding to singly end-labeled fragments cleaved by CELI at the mutation site. Mutant individuals identified from pools, sequenced. Information and analysis returned to 200 bp User, along with Stock Center numbers for ordering seed. 95bp IR800