* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell - Fair Lawn Schools
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
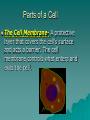
Mr. Altorfer Life Science The Diversity of Cells Pages 60 to 67 Cells and the Cell Theory Cell: A cell is the smallest unit that can perform all the processes necessary for life. Cells and the Cell Theory Robert Hooke- In 1665 he looked at a piece of cork under his microscope. He saw little boxes in the cork that he called “CELLS.” Cells and the Cell Theory Anton van Leewenhoek- (1673) A Dutch merchant who built microscopes as a hobby. Cells and the Cell Theory Euglena Yeast Blood Cells Bacteria Cells Cells and the Cell Theory Matthias Schleiden- (1838) A German scientist who concluded that all plants are made of cells. Cells and the Cell Theory Theodor Schwann- (1839) A German scientist who concluded that all animals are made of cells. Cells and the Cell Theory Rudolf Virchow- (1858) A German doctor who concluded that all cells come from other cells. Cells and the Cell Theory The Cell Theory: – ALL organisms (living things) are made of one or more cells. – The cell is the basic unit of all living things. – All cells come from already existing cells. (other cells) THIS IS THE MOST IMPORTANT THEORY IN LIFE SCIENCE!!!!!! Cell Size Most cells are very small! Cells have to be small. If cells become too big, they are unable to get nutrients and waste material in or out of the cell! Parts of a Cell The Cell Membrane- A protective layer that covers the cell’s surface and acts a barrier. The cell membrane controls what enters and exits the cell. Parts of a Cell Organelles- Small parts of the cell that perform different jobs inside a cell. Organelles are similar to the organs in your body, only smaller. Examples: Nucleus, mitochondria. We will learn more about these in a few days. Relax! Parts of a Cell DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)- All cells contain genetic material in the form of DNA. DNA carries the information necessary for the cell to function and to make more copies of the cell. Two Kinds of Cells Prokaryotic Cells- Single celled organisms that do not have a an organized nucleus or membranebound organelles. Examples: Bacteria and Archaea Bacteria Archaea Two Kinds of Cells Eukaryotic Cells- Cells that contain a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotes- Organisms that contain eukaryotic cells. – Examples: People, plants, algae and Protists (amoeba) Amoeba Algae