* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Chromatophore wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
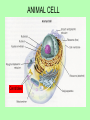
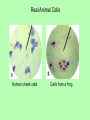
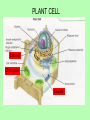
Animal cells vs. Plant cells: Interestingly different, Surprisingly similar! ANIMAL CELL Centrioles Centrioles •Nonmembrane-bound organelles that occur in pairs just outside the nucleus of animal cells. •Each centriole is composed of a cylinder or ring of 9 sets of microtubules. •They organize cell division. Also give rise to cilia and flagella, structures that allow a cell to move and propel itself. •Found only in animal cells. Real Animal Cells Human cheek cells Cells from a frog PLANT CELL Cell wall Chloroplast Vacuole Cell wall •Cell walls lie outside the cell membrane •They are porous and allow water, oxygen, and carbon dioxide to pass through easily •The cell wall provides support and protection for the cell. •Plant cell walls are made mainly of cellulose with fibers of protein to help strengthen the wall. Chloroplast •Organelles that capture energy from sunlight and convert it into chemical energy in a process called photosynthesis •Plants can’t move to get food to eat for energy, so they must get energy from the sun •Inside the chloroplast are stacks of other membranes that contain the pigment chlorophyll (a green pigment, which is why most plants are green) Vacuole •A membrane-bound, fluidfilled sac that occupies much of the volume of a plant cell. •The pressure of the central vacuole makes it possible for plants to support heavy structures like leaves and stems •Also functions as a place to store water, since plants can’t move to get water like animals can. The Plastids • Two Main Types of Plastids We Will Study • Leucoplast: Store Starch, typically found in root cells. Ex: Potato • Chromoplast: Store Pigments which help, but cannot do photosynthesis on their own. Chromo = Color (Red/Orange/Yellow) • Ex: Tomato Skin Cells Walls and Membranes • Important to note: • Plant cells have a cell wall and a cell membrane = both • Animal cells only have a cell membrane, but no walls. So which structures are found in both animal and plant cells? Which are found only in plant cells? Which are found only in animal cells? Let’s use a Venn Diagram to compare the two types of cells.