* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chp 6 Cells Part1
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
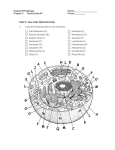
Tour of the Cell AP Biology 2007-2008 Types of cells Eukaryote animal cells AP Biology Prokaryote bacteria cells Eukaryote plant cells Why organelles? Specialized structures mitochondria specialized functions cilia or flagella for locomotion Containers partition cell into compartments create different local environments chloroplast separate pH, or concentration of materials distinct & incompatible functions lysosome & its digestive enzymes Membranes as sites for chemical reactions AP Biology Golgi unique combinations of lipids & proteins embedded enzymes & reaction centers chloroplasts & mitochondria ER Cells gotta live! What jobs do cells have to do? building proteins proteins control every cell function make energy for daily life for growth build more cells growth reproduction repair AP Biology Why study protein production? proteins cells DNA AP Biology Repeat after me… organism DNA gets the glory, but Proteins do all the work! Building Proteins Organelles involved nucleus ribosomes endoplasmic reticulum (ER) Golgi apparatus vesicles The Protein Assembly Line nucleus AP Biology ribosome ER Golgi apparatus vesicles TO: endoplasmic reticulum nucleus protein on its way! DNA RNA TO: vesicle TO: TO: vesicle TO: ribosomes finished protein protein Golgi apparatus Making Proteins AP Biology Putting it together… nucleus nuclear pore Making proteins cell membrane protein secreted rough ER ribosome vesicle proteins smooth ER AP Biology transport vesicle cytoplasm Golgi apparatus Cells gotta live! What jobs do cells have to do? make proteins proteins control every cell function make energy for daily life for growth build more cells growth reproduction repair AP Biology ATP Cells need power! Making energy take in food & digest it take in oxygen (O2) make ATP remove waste ATP AP Biology 1960 | 1974 Lysosomes Function Christian de Duve little “stomach” of the cell digests macromolecules “clean up crew” of the cell cleans up broken down organelles Structure vesicles of digestive enzymes Where old organelles go to die! AP Biology only in animal cells Lysosomal enzymes Lysosomal enzymes work best at pH 5 organelle creates custom pH how? proteins in lysosomal membrane pump H+ ions from the cytosol into lysosome why? enzymes are very sensitive to pH why? enzymes are proteins — pH affects structure AP Biology why is this an adaptation: digestive enzymes which function at pH different from cytosol? digestive enzymes won’t function well if some leak into cytosol = don’t want to digest yourself! But sometimes cells need to die… Lysosomes can be used to kill cells when they are supposed to be destroyed some cells have to die for proper development in an organism apoptosis “auto-destruct” process lysosomes break open & kill cell ex: tadpole tail gets re-absorbed when it turns into a frog ex: loss of webbing between your fingers during fetal development ex: self-destruct of cancerous cell AP Biology syndactyly Fetal development 6 weeks 15 weeks AP Biology When things go wrong… Diseases of lysosomes are often fatal digestive enzyme not working in lysosome picks up biomolecules, but can’t digest one lysosomes fill up with undigested material grow larger & larger until disrupts cell & organ function lysosomal storage diseases more than 40 known diseases example: AP Biology Tay-Sachs disease build up undigested fat in brain cells