* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 7-Cells and the Microscope
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
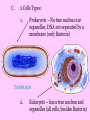
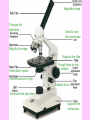
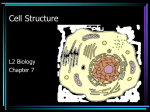
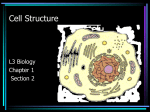
Chapter 7 – The Cell I. A View of the Cell A. Contributing Scientists who came up with ideas about the cell: 1. Hooke (1665) – first saw cork cells & named the tiny boxes “cells” after monk’s rooms in a monastery 2. Leeuwenhoek (1683) – saw cells using a microscope which he invented 3. Schleiden (1838) – said cells compose every part of a plant 4. Schwann (1839) – said cells compose every part of an animal 5. B. Virchow (1855) – said cells only come from other cells The Cell Theory – 3 parts: 1. All organisms are made of 1+ cells 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure & organization of all living organisms (a cell is the simplest living part) 3. All cells come from pre-existing cells, & pass copies of genetic information on to daughter cells C. 2 Cells Types: 1. Prokaryote – No true nucleus nor organelles; DNA not separated by a membrane (only Bacteria) The Scale of Life 2. Eukaryote – has a true nucleus and organelles (all cells, besides Bacteria) II. The Cell is like a Factory A. Cell/Plasma Membrane (Doors): maintains homeostasis by regulating what goes in & out of the cell (selectively permeable) B. Nucleus (Boss): contains directions for the cell’s operations C. Nucleolus (Boss’ Assistant): inside nucleus, it makes ribosomes D. Chromatin (Blueprints): inside nucleus; are strands of DNA with directions for cell E. Cytoplasm (Air): jellylike fluid that fills the cell F. Mitochondria (Generator): makes energy (ATP) for the cell/our body G. Golgi Body (Assembly Line): packages cell products 1. Vesicles (trucks): distribute cell products H. Centriole (Boss’ wife): helps in cell reproduction I. Cytoskeleton (steel frames in brick walls): stick-like microtubules & microfilaments support the cell like a skeleton J. Lysosome (cleanup crew w/ garbage cans): digest wastes K. Ribosomes (Cooks): make protein L. Endoplasmic Reticulum (Vending Machines): 1. Smooth ER (almonds): no ribosomes, makes fats 2. Rough ER (cheese): has ribosomes, makes proteins M. Movement Organelles 1. Cilia (conveyor belt): parts that sway 2. hair-like Flagella (forklift): whip-like tail III. Parts found only in Plant Cells: A. Cell Wall (Bricks): – rigid for support B. Vacuole (Warehouse): – filled w/ fluid & stores water and waste C. Chloroplast (Solar Panels): makes glucose through photosynthesis; green due to chlorophyll Let’s check out these for Review: The Cell Song https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rABKB5aS2Zg Cells Cells – Parts of the Cell https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-zafJKbMPA8 Cells from Other Cells https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BTicXXxzQA4 Chapter 7 – The Microscope Before microscopes were invented, people believed that diseases were caused by curses and spirits I. Types of Microscopes (2) A. Light Microscope – has a series of lenses to magnify objects in steps 1. light passes thru object being observed 2. object can be living or dead 3. magnifies up to 1500x (ours 400x) 4. Total Magnification = Eyepiece x Lens B. Electron Microscope (EM) – a beam of electrons is focused by magnets to enlarge an image magnifies objects up to 500,000x object is placed in a vacuum, so it is often dead when viewed costs about $25,000 1. Transmission EM (TEM) – electrons pass thru object; 2D views 2. Scanning EM (SEM) – electrons bounce off surface of object; 3D views 3. Scanning Tunneling EM (STM) – electrons “tunnel” through living specimens; sees atoms 4. Atomic Force Microscope (AFM) – measures force b/t probe and specimen II. Parts of the Microscope: Magnifies image Changes the objectives Used to carry the microscope Magnify the image Supports the slide Holds slide in place Rough focus for low & medium Controls amount of light Detailed focus Illuminates the specimen Supports the microscope III. Using the Microscope 1. Turn the light switch on and put the slide onto the stage 2. Start with the lens in low power 3. Focus the specimen using coarse, then fine adjustment 4. Rotate the nosepiece to medium power 5. Focus the specimen using coarse, then fine adjustment 6. Rotate the nosepiece to high power 7. Focus the specimen using FINE adjustment ONLY