* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 11 - Tissues (Animal & Plant)
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
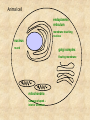
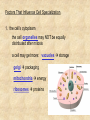
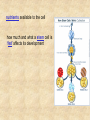
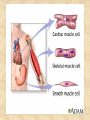
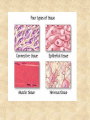
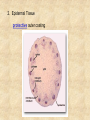
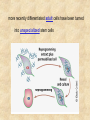
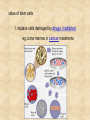
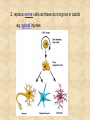
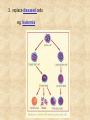
Draw a cell 1. fold a page in half 2. on the top half draw a circle 3. on the bottom half draw a rectangle 4. each represents a cell type label one ‘animal and one ‘plant’ now add the following (without looking at your notes) read the list and plan ahead before starting nucleus endoplasmic reticulum chloroplast centriole golgi apparatus cell wall vacuole mitochondria not all parts will be in both cells Animal cell endoplasmic reticulum membrane touching nucleus nucleus round golgi complex floating membrane mitochondria sausage shaped – interior structure endoplasmic reticulum nucleus chloroplast oval with green insides golgi complex vacuole large, empty mitochondria cell wall thick, outside membrane Cell Specialization and Tissues sexually reproducing organisms start out life as a fertilized egg cell a zygote mitosis allows this one cell to divide into many billions of cells without cell specialization you would just be a big ball of identical cells all doing identical things cell specialization occurs when any one cell differs from those around it in appearance or function Factors That Influence Cell Specialization 1. the cell’s cytoplasm the cell organelles may NOT be equally distributed after mitosis a cell may get more: vacuoles storage golgi packaging mitochondria energy ribosomes proteins 2. environmental conditions temperature cells are exposed to may influence expression of genes all cells in the Siamese cat have the potential to make the black pigment, but only the cells below 36oC do so nutrients available to the cell how much and what a stem cell is ‘fed’ affects its development 3. the effect of neighbouring cells where a cell is in a multicellular organism influences how it behaves each cell receives chemical signals from the cells around it a cell receives different signals based on where it is in the organism these signals then cause the cell to differentiate appropriately it is why we have a thumb and four fingers, rather than just all fingers and no thumb Types of Animal Tissues 1. Epithelial these tissue form a layer around other tissues a. skin epithelia flat cells that form a semi-permeable barrier between the body and the outside world b. columnar epithelial cells lining the intestine, stomach, glands secrete mucous, absorb materials 2. muscle a. skeletal muscle made up of long cells that align to look striped attach to bones to allow movement can contract quickly and with force b. smooth muscle made up of cells that do not look striated (striped) found in blood vessels, digestive organs contract slowly but can sustain contractions c. cardiac muscle found only in the heart appear to be striated unevenly work together, all contract at once do NOT get tired 3. nervous consist of neuron cells which have long projections to receive & transfer signals function to coordinate body actions 4. connective a. bone consists of protein hardened by calcium needed for protection support & movement b. fat or adipose tissue large cells around organs and under skin provide energy storage and insulation whale blubber c. blood red blood cells carry oxygen to cells white blood cells attack invaders to protect the body platelets release fibrin to clot the blood Types of Plant Tissues 1. Meristematic Tissue not dividing unspecialized tissue capable of dividing by mitosis dividing only found in root tips, buds and cambium not dividing 2. Epidermal Tissue protective outer coating involved in water entering roots and gases entering or leaving leaf 3. Ground Tissue provides support for stem all 3 are ground tissue storage of food and water in roots site of photosynthesis in leaves all the cells with chloroplasts 4. Vascular tissue xylem moves water & dissolved minerals up from the roots series of tubes moving water & minerals up phloem moves dissolved sugars (food) down from the leaves series of tubes moving water & sugars down xylem & phloem are found together in a vascular bundle cambium is meristematic tissue that makes xylem & phloem Comparing animal and plant tissues: Explain why each animal tissue corresponds to the given plant tissue plant epidermal animal epithelial what they have in common both protect both allow entry animals absorb, plants allow entry ground tissue connective both support both store vascular tissue muscle both transport (remember arteries & veins are muscles tissue) meristematic tissue none all animal tissue can divide & grow Challenges with cell specialization a. regeneration if a salamander loses a limb it can regenerate but humans can not why before birth all stem cells are set in humans b. manipulating stem cells unspecialized stem cells can be taken from an unwanted embryo problems of moral issues more recently differentiated adult cells have been turned into unspecialized stem cells value of stem cells 1. replace cells damaged by drugs / radiation eg. bone marrow in cancer treatments 2. replace nerve cells as these do not grow in adults eg. spinal injuries 3. replace diseased cells eg. leukemia 4. replace worn out organs eg. grow a bladder in the lab from own cells