* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Test Review Questions
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
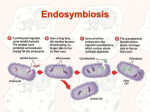
Chapter 17/19.3 Review 1. Natural selection acts on _______________________. 2. Natural selection acts on the _______________________, not a single gene. 3. A _______________________ is a group of individuals of the ___________ species that live in the same area and interbreed. 4. True or false? A gene pool consists of all genes including all the different alleles, that are present in a population. 5. True or False? Allele frequency has to do with whether the allele is dominant or recessive. 6. List the 3 sources of genetic/heritable variation. 7. A __________________________________ trait has 2 alleles, and can only have _____________ phenotypes. 8. A trait controlled by two or more genes is a _____________________ trait. How many phenotypes does this produce?___________________. This typically produces a ___________-______________ curve. 9. What are three ways natural selection can affect phenotype distribution? 10. 11. Directional selection occurs when a. b. c. d. e. the environment controls which organisms will survive. humans determine which organisms will survive. the extremes of the population have a lesser chance to survive. the extremes of the population have a better chance to survive. the organisms on one extreme of the population have a better chance to survive than those on the other extreme. 12.The random change in allele frequency within a small population is called? 13.Genetic equilibrium is another way to state the _______________________ principle. 14.In population genetics, a _________________________occurs when the effective population size sharply decreases to a small percentage of the original. The immediate is a decrease genetic diversity. 15.Write the Hardy-Weinberg principle as a mathematics equation. 16. 17.The process that creates new species is _______________________. 18.List 3 types of reproductive isolation: 19.Speciation in Darwin’s Finches: Founders arrive on the Galapagos Separation of populations Changes in the gene pools of each population Reproductive Isolation Ecological Competition Continued Evolution 20.Earths early atmosphere was composed of __________________________. 21.Observations supporting Endosymbiotic theory: 1. Size & Structure – mitochondria are about the same size as most bacteria & its membrane is like that of aerobic bacteria 2. Genetic material- mitochondria & chloroplasts have circular DNA similar to bacterial DNA & genes different from nuclear DNA 3. Ribosomes in mitochondria & chloroplasts have similar size & structure of bacterial DNA 4. Reproduction- Like bacteria, mitochondria & chloroplasts reproduce by binary fission; Takes place independently of cell cycle of the host cell 22. Endosymbiotic theory states chloroplasts came from ______________________ and mitochondria evolved from____________________________. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Phenotypes Organism Population/species True False Mutation; genetics recombination (independent assortment, crossing-over, some alleles from dad and some from mom.), lateral gene transfer (transformation) 7. Single-gene; 2 or 3 8. Polygenic/many/bell-shaped 9. Directional Selection Stabilizing Selection Disruptive Selection 10.3 examples 11.E. 12.Genetic drift 13.Hardy-Weinberg 14.population bottleneck 15. Hardy Weinberg equation 16.See slide 17.Speciation….key part is reproductive isolation 18. 19. slide 20. hydrogen cyanide, CO2, CO, N2, hydrogen sulfide, H2O vapor 21. Size & Structure – mitochondria are about the same size as most bacteria & its membrane is like that of aerobic bacteria Genetic material- mitochondria & chloroplasts have circular DNA similar to bacterial DNA & genes different from nuclear DNA Ribosomes in mitochondria & chloroplasts have similar size & structure of bacterial DNA Reproduction- Like bacteria, mitochondria & chloroplasts reproduce by binary fission; Takes place independently of cell cycle of the host cell 22. Endosymbiotic prokaryotes which were photosynthetic/ endosymbiotic prokaryotes that used oxygen 1. If 56 out of 300 individuals in a population express the recessive phenotype, A. What percent of the population are homozygous dominant? B. What is the frequency of the heterozygous individuals? C. What is the frequency of dominant allele? D. What is the frequency of the recessive allele?