* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Catalytic triad wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
15-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid wikipedia , lookup
Specialized pro-resolving mediators wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
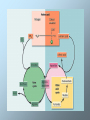
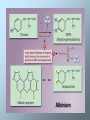
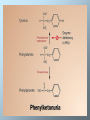
Amino Acid Oxidation and the Production of Urea Fate of Ammonium Three major reactions in all cells • Carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase I – two ATP required - one to activate bicarbonate, one to phosphorylate carbamate • Glutamate dehydrogenase – reductive amination of alpha-ketoglutarate to form glutamate • Glutamine synthetase – ATP-dependent amidation of gamma-carboxyl of glutamate to glutamine The Urea Cycle In ureotelic organisms the urea cycle disposes of approximately 90% of surplus nitrogen. Urea is formed from ammonia, CO2, and aspartate in a cyclic pathway referred to as the urea cycle. The urea cycle is a mechanism designed to convert NH4+ to urea, a less toxic molecule. Note that citrulline is transported across the inner membrane by a carrier for neutral amino acids. Ornithine is transported in exchange for H+ or citrulline. Fumarate is transported back into the mitochondrial matrix. Because the urea cycle was discovered by Hans Krebs and Kurt Henseleit, it is often referred to as the Krebs urea cycle or the Krebs-Henseleit cycle. Hans Krebs Urea synthesis begins with the formation of carbamoyl phosphate. The substrates for this reaction, which is catalyzed by carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I, are NH4+ and HCO3- . Because two molecules of ATP are required in the carbamoyl phosphate synthesis, this reaction is essentially irreversible. Carbamoyl phosphate subsequently reacts with ornithine to form citrulline. This reaction, which catalyzed by ornithine transcarbamoylase, is driven to completion because of the release of phosphate from carbamoyl phosphate. Citrulline is transported to the cytoplasm, where it reacts with aspartate. The amino group of aspartate provides the second nitrogen that is ultimately incorporated into urea. This reaction is catalyzed by argininosuccinate synthase. Argininosuccinate lyase subsequently cleaves arginosuccinate to form arginine (the immidiate precursor of urea) and fumarate. In the final reaction of the urea cycle, arginase catalyzes the formation of urea. Ornithine, the other product of this reaction, is transported into the mitochondrial matrix, thus enabling the urea cycle to continue. The Urea Cycle Is Energetically Expensive The overall equation of the urea cycle is 2NH4+ + HCO3- + 3ATP4- + H2O urea + 2ADP3- + 4Pi2- + AMP2- + 5H+ The synthesis of one molecule of urea requires four high-energy phosphate groups. Two ATPs are required to make carbamoyl phosphate, and one ATP is required to make argininosuccinate. In the latter reaction, however, the ATP undergoes a pyrophosphate cleavage to AMP and pyrophosphate, which may be hydrolyzed to yield two Pi. After its transport back into the mitochondrial matrix, fumarate is hydrated to form malate, a component of the citric acid cycle. The oxaloacetate product of the citric acid cycle can subsequently be used in energy generation, or it can be converted to glucose or aspartate. The relationship between the urea cycle and citric acid cycle, often referred to as Krebs bicycle. Disorders of Amino acid Catabolism Alcaptonuria caused by a deficiency of homogentisate oxidase. Large quantities of homogentisate, the substrate for defective enzyme, are excreted with urine. Homogentisate turns black when it is oxydized as the urine is exposed to air. Alcaptonuria is not innocuous, since alcaptonic patients develop arthritis in later life. In addition, the pigment accumulates gradually and evenly darkens the skin. Albinism In this condition the enzyme tyrosinase is deficient. Consequently, melanin, a black pigment found in skin, hair, and eyes, is not produced. It is formed from tyrosine in several cell types (e.g. the melanocytes). In such cells tyrosinase converts tyrosine to DOPA and DOPA to dopaquinone. The latter product condense to melanin. Because of the lack of pigment, albinos are extremly sensitive to sunlight. In addition to their susceptibility to skin cancer and sunburn, the eyesight of albino is often adversely affected. Phenylketonuria is caused by deficiency of phenylalanine hydroxylase. If this condition is not treated immediately after birth, mental retardation and other forms of irreversible brain damage ensue. This damage results from the accumulation of phenylalanine. When it present in excess, phenylalanine undergoes transamination to form phenylpyruvate, which is also subsequently converted to phenyllactate and phenylacetate. Large amounts of these molecules are excreted in the urine. Phenylacetate gives the urine its characteristic musty odor. Phenylketonuria is treated with a low phenylalanine diet. In maple syrup urine disease, also called branched chain ketoaciduria, the keto acids derived from leucine, isoleucine, and valine accumulate in large quantities in blood. Their presence in urine imparts a characteristic odor that gives the malady its name. All tree keto acids accumulate because of a deficient branched chain keto acid dehydrogenese complex. If left untreated affected individuals experience vomiting, convulsions, severe brain damage, and mental retardation. Death than occurs before one year of age. Treatment consists of rigid dietary control. TESTS FOR TOPIC CONTROL 1. A patient has an allergic reaction that is accompanied by itches, edemata, and rednesses. What biogenic amine concentration increases in the tissues? A Tryptamine B Taurine C Serotonin D Putrescine E Histamine 2. Proteolytic enzymes of the GI tract catalyze protein hydrolysis. Point the bond that is broken up by these enzymes: A Ester B Peptide C Hydrogen D Phosphodiester E Glycosidic 3. Digestion of proteins in the stomach begins under the action of pepsin that is secreted in a form of pepsinogen – inactive precursor. The conversion of pepsinogen to pepsin is fulfilled by means of the N-end peptide removal under the action of: A Acetic acid B Bile acid C Sulphuric acid D Hydrochloric acid E Amino acids 4. Gastric juice pH in milk-fed children varies in the limits of 4.0 - 5.0. Name a gastric juice enzyme that is active under these conditions. A Elastase B Pepsin C Chymotrypsin D Trypsin E Renin 5. Biogenic amines undergo deamination under the action of a certain enzyme. Point it. A Decarboxylase B Monoamine oxidase C Amino acid dehydrogenase D Alanine transaminase E L-amino acid oxidase 6. Dysfunction of the liver is observed in a patient. What biochemical index is to be determined in the blood for estimation of the liver state? A LDH1 B Aldolase C АLТ D Creatine phosphokinase E Lipase 7. Ammonia is generated in different tissues and organs and neutralized in the liver by converting into urea. What amino acid transports it from skeletal muscles to the liver? A Glycine B Histidine C Alanine D Serine E Aspartic acid 8. The main way of ammonia detoxication is the urea synthesis. This biochemical process begins from the formation of: A Carbamoyl phosphate B Citrulline C Arginine D Ornithine E Pyrophosphate 9. Aminotransferases are the enzymes which transfer amino groups from one compound to another. Point the acceptor of amino groups. A Butyric acid B Lactic acid C Succinate D Acetone E α-Ketoglutaric acid 10. In a patient the amino acid transport in the intestine cells is decreased. What substance participates in the amino acid transport? A Glutathione B Antiserine C Amylase D Ornithine E Alanine