* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Section 6-1
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Essential gene wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
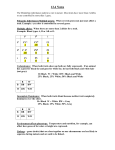
Section 6-1 Human Inheritance Patterns of Human Inheritance • Traits controlled by single genes with only two alleles – Height in pea plants – Widow’s peak – Stuff from last unit • Multiple Alleles – Some traits controlled by a single gene with more than two alleles • Blood type – controlled by three alleles – Type A – IAIA or IAi – Type B – IBIB or IBi – Type AB - IAIB – Type O - ii • Traits controlled by many genes – At least four genes are responsible for height in people – Skin color is controlled by three genes • Each gene is controlled by two alleles • Therefore almost endless combinations Sex Linked Traits • Male or Female – XX = Female – XY = Male • Sex Linked Genes – Located on the X and Y chromosomes – Males more likely to have recessive sex linked traits