* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download lecture12
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
BRCA mutation wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
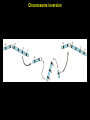
Mutation & genetic variation Mutations Mutations gene – stretch of dna that codes for a distinctive type of rna or protein allele – versions of the same gene that differ in their base sequence mutation – any change in the base sequence of dna Types of mutations Point mutation Frameshift mutation Gene duplication Chromosome inversion Polyploidy Point mutation Point mutations are single base substitutions in DNA Point mutation Genetic code Frameshift mutation Frameshift mutation Gene duplication Gene duplication Duplicated loci can: -retain their original function and provide an additional copy of the parent locus -gain a new function through mutation & selection -become functionless pseudogenes Chromosome inversion Chromosome inversion Inversions change gene order and decrease the frequency of crossing over As a result, the alleles inside the inversion tend to be inherited as a unit Polyploidy Polyploidy Polyploid populations are reproductively isolated from their parental species Fitness effects of mutation Mutation rate Species Taxon mutations/genome/ generation E. coli bacteria S. acidocaldarius archaea S. cerevisiae fungi 0.0025 0.0018 0.0027 C. elegans D. melanogaster M. musculus H. sapiens 0.0360 0.1400 0.9000 1.6000 roundworm insect mammal mammal Mutation rate Mutation rates vary among species because of differences in the number of cell divisions that take place prior to gamete formation Human Fruit fly 400 cell divisions 25 cell divisions Polymorphism If more than one allele exists at a particular locus, a population is said to be polymorphic at that locus Polymorphism One third to one half of all coding loci are polymorphic in a typical population Why are populations genetically diverse? Selectionist theory - genetic diversity maintained by natural selection Neutral theory - genetic diversity maintained because it is not eliminated by selection