* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Brickell Academy Life Science
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
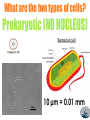
Directions Watch the video about the wacky history of the cell theory. It is located on my website. Your notes… Place all notes on right side of N21. You should know the three principles of the cell theory, the scientists that are important in the discovery of cells, and the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. I suggest sketch notes, but you can use whatever format you like. What are the three principles to the cell theory? All organisms are composed of A ________ one or more cells. Basic ________ units of structure, organization B and function in all organisms. C Cells ________ come from preexisting cells. Who was Zacharias Janssen? He made the first known _______________ compound microscope in 1595. Who was Anton VanLeeuwenhoek? He made the first __________ single lens microscope and discovered one-celled organisms including, bacteria in 1676. Who was Robert Hooke? He used microscopes to look at cork and coined the term __________ cells in 1665. Who was Matthias Schleiden? plants He concluded that all __________ are made of cells in 1838. Who was Theodor Schwann? He concluded that all animals __________ are made of cells in 1839. Who was Rudolph Virchow? He concluded that _______ cells must come from ______________________ preexisting cells in 1855. Who was Robert Brown? A botanist that looked at many different plant cells and noticed that they each had a dark structure that he called a _____________ in 1831. nucleus What are the two types of cells? Prokaryotic (NO NUCLEUS) Unicellular (can only be one • _________________ cell) circular • DNA (genetic material) is ___________ and in the cytoplasm. • Examples: Bacteria and Archaea What are the two types of cells? Prokaryotic (NO NUCLEUS) 10 µm = 0.01 mm What are the two types of cells? Eukaryotic (NUCLEUS) • __________________________________ Uni- and Multicellular (can have specialized cells) linear • DNA (genetic material) is _____________ and in the nucleus. • Examples: Protista, Fungi, Plant, and Animal kingdoms What are the two types of cells? Eukaryotic (NUCLEUS) Take a minute to update your notes and illustrate the vocabulary in your reference section (underline in pink). Cell and Cell Theory (R8) Eukaryote (R12) Microscope and Multicellular (R18) Prokaryote (R22) Unicellular (R27) Your notes… Do you have the three principles of the cell theory, the scientists that are important in the discovery of cells, and the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? If you answered no, go back and fix your notes.