* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Climate Change
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change wikipedia , lookup
Climate resilience wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
German Climate Action Plan 2050 wikipedia , lookup
Climate change denial wikipedia , lookup
Heaven and Earth (book) wikipedia , lookup
Michael E. Mann wikipedia , lookup
Global warming controversy wikipedia , lookup
Climate change adaptation wikipedia , lookup
Numerical weather prediction wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Global warming hiatus wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit documents wikipedia , lookup
Instrumental temperature record wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric model wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on Australia wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate engineering wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Years of Living Dangerously wikipedia , lookup
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
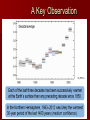
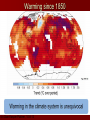
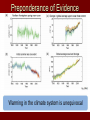
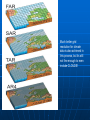
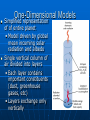
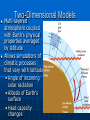
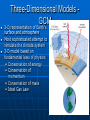
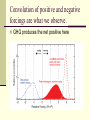
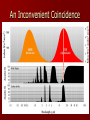
IPCC Climate Change Report Moving Towards Consensus Based on real world data IPCC Consensus process is Conservative by Nature The most Recent (2013) IPCC report is, by far. The most comprehensive compared to the previous 4 Climate Change 2013 observations FAR 1990 SAR 1995 TAR 2001 AR4 2007 AR5 2013 11 Chapters 11 Chapters 14 Chapters 11 Chapters 14 Chapters paleoclimate sea level clouds carbon cycle regional change A Key Observation Warming since 1850 c/o Gian-Kasper Plattner, 10-8-13 Preponderance of Evidence Climate Modeling Evolution We have the Sun, some Rain and some CO2 pollution, that’s it Climate Modeling Evolution Now we add in Clouds, the land surface, and ice reflectivity Climate Modeling Evolution In the First Assessment Report (FAR – 1990) the Ocean as CO2 sink was now added in Climate Modeling Evolution By the mid 1990s sulfur emissions from volcanoes and/or industry were added as cooling agents (this is because of Pinatubo)) and the role of surface ocean current transport was more strongly considered Pinatubo Ash Eruption Climate Modeling Evolution By 2001 aerosol scattering (very complicated) is now incorporated as is deep ocean transport, the actual carbon cycle and the role that rivers play in the hydrological cycle Climate Modeling Evolution Finally atmospheric chemistry is considered in the 2007 report along with reflectivity changes on the Earth due to changing vegetation patterns Much better grid resolution for climate data is also achieved in this process, but its still not fine enough to even include CLOUDS! Data-Model Comparisons Models constructed to simulate Modern circulation • Changes based on Earth History inserted in model • Climate output compared with observations One-Dimensional Models Simplified representation of of entire planet • Model driven by global mean incoming solar radiation and albedo Single vertical column of air divided into layers • Each layer contains important constituents (dust, greenhouse gases, etc) • Layers exchange only vertically Two-Dimensional Models Multi-layered atmosphere coupled with Earth’s physical properties averaged by latitude Allows simulations of climatic processes that vary with latitude • Angle of incoming solar radiation • Albedo of Earth’s surface • Heat capacity changes Three-Dimensional Models GCM 3-D representation of Earth’s surface and atmosphere Most sophisticated attempt to simulate the climate system 3-D model based on fundamental laws of physics: • Conservation of energy • Conservation of momentum • Conservation of mass • Ideal Gas Law Model Resolution Can’t image New Zealand, for example – (2° lat x 3° long) – this deficiency matters! Steady State Tub If flux of tracer into and out of reservoir are equal, the system is at steady state Residence Time Time it takes for tracer to pass through tub • Residence time = reservoir size/flux Residence time of tracer typically > mixing time of the ocean (1500 y) In this way, the oceans are an enormous buffer (on short time scales) Basic Approach double CO2 and model planetary response Convolution of positive and negative forcings are what we observe. GHG produces the net positive here An Inconvenient Coincidence Equilibrium Temperature Planet radiates as a blackbody in TE with incoming solar radiation: A = Albedo; L = 1370 watts per sq meter T = 278(1-A)4 T = 255K for A=0.32 This is not the right answer compared to observations The Role of the Atmosphere Fo = incident flux Ts = transmission % incoming Tt = transmission % outgoing Fg = Flux from ground Fa = Flux from the atmosphere. Fo = Fa + TtFg top of atmosphere equilibrium Let Fa = Fo –TtFg Fg = Fa + TsFo outgoing ground equilibrium F g = Fo https://www.youtube.com/watch? v=otRPf3rRwZk