* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2. Intro to Proteins
Homology modeling wikipedia , lookup
Protein folding wikipedia , lookup
Protein domain wikipedia , lookup
Bimolecular fluorescence complementation wikipedia , lookup
Cooperative binding wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Protein mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
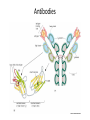
PROTEINS INTRODUCTION Useful Proteins • There are thousands and thousands of different combinations of amino acids that can make up proteins and that would increase if each one had multiple shapes • Proteins usually have only one useful conformation • Natural selection has eliminated proteins that do not perform a specific function in the cell Functions / importance of Proteins • • • • • • • • • • • Type Structural Contractile Transport Storage Hormonal Enzyme Protection Energy Signalling Receptors Motor proteins Examples tendons, cartilage, hair, nails muscles hemoglobin, albumin ferritin eg. insulin, growth hormone eg. hydroxylases immunoglobulins 4.1 k.cal/gm Motor kinesin 8 Protein Families Enzymes • Have similarities in amino acid sequence and 3-D structure • Have similar functions such as breakdown proteins but do it differently Proteins at Work • The conformation of a protein gives it a unique function • To work proteins must interact with other molecules, usually 1 or a few molecules from the thousands to 1 protein • Ligand – the molecule that a protein can bind • Binding site – part of the protein that interacts with the ligand – Consists of a cavity formed by a specific arrangement of amino acids Ligand Binding Enzymes as Catalysts • Enzymes are proteins that bind to their ligand as the 1st step in a process • An enzyme’s ligand is called a substrate – May be 1 or more molecules • Output of the reaction is called the product • Enzymes can repeat these steps many times and rapidly, called catalysts Enzymes at Work • Lysozyme is an important enzyme that protects us from bacteria by making holes in the bacterial cell wall and causing it to break • Lysozyme adds H2O to the glycosidic bond in the cell wall • Active site is a special binding site in enzymes where the chemical reaction takes place Antibodies • Y-shaped molecules with 2 binding sites at the upper ends of the Y • The loops of polypeptides on the end of the binding site are what imparts the recognition of the antigen • Changes in the sequence of the loops make the antibody recognize different antigens specificity Antibodies Antibody Family • A family of proteins that can be created to bind to almost any molecule • Antibodies (immunoglobulins) are made in response to a foreign molecule ie. bacteria, virus, pollen… called the antigen • Bind together tightly and therefore inactivates the antigen or marks it for destruction Motor Proteins • Proteins can move in the cell, say up and down a DNA strand but with very little uniformity • The hydrolysis of ATP can direct the the movement as well as make it unidirectional – The motor proteins that move things along the actin filaments or myosin Protein Machines • Complexes of 10 or more proteins that work together such as DNA replication, RNA or protein synthesis, transmembrane signaling etc. • Usually driven by ATP or GTP hydrolysis