* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetics Vocabulary Spring 2011
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
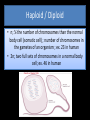
Genetics Vocabulary Spring 2014 Venable Biology Genetics and Heredity • The study of heredity • The passing of traits from parents to offspring Meiosis / Gametes • The making of sex cells • Gamete – sex cell; examples are sperm, egg, pollen, ovule Zygote • A fertilized egg ; two gametes become one Fertilization / Pollination • The fusing or uniting of two gametes (into 1 cell) ; forms a zygote or seed • When pollen reaches the stigma of the female pistil of a flower Stamen / Pistil • Male reproductive part of the flower ; made of the anther (holds pollen) and filament • Female reproductive of the flower ‘ made of the stigma (sticky top portion), style, and ovary Chromosomes • Strands of genetic information found in the nucleus of a cell Haploid / Diploid • n; ½ the number of chromosomes than the normal body cell (somatic cell) ; number of chromosomes in the gametes of an organism ; ex. 23 in human • 2n; two full sets of chromosomes in a normal body cell; ex. 46 in human Allele • An alternative form of a gene (one member of a pair) that is located at a specific position on a specific chromosome ; each for a particular trait • For example, the gene for seed shape in pea plants exists in two forms, one form or allele for round seed shape (R) and the other for wrinkled seed shape (r). Trait • Characteristics inherited from two parents ; A genetically determined characteristic or condition Genes • An allele that codes for a particular trait ; Genes are segments of DNA located on chromosomes. Genes exist in alternative forms called alleles. Genotype / Phenotype • Gene combination that determines a trait ; the genetic makeup of an organism • The physical trait created by the genotype ; an organism's expressed physical traits Dominant / Recessive • Allele that is seen of present ; represented with a capital letter • Allele that is masked / not seen unless paired with another recessive allele ; lower case letter Dominant Alleles: T, G, A, B Recessive Alleles: t, g, a b Gregor Mendel • Austrian monk who studied the garden pea plant (7 different traits studied); “The Father of Genetics” Homozygous / Heterozygous • Genotype were both alleles paired up are identical ; ex. TT, tt • Genotype were both alleles paired up are opposite ; ex. Tt Sex Chromosomes • The 23rd pair of paired chromsomes in an human somatic cell (The 1-22 pair are referred to as AUTOSOMES). • The sex chromsomes may be X or Y ; human males all have a 23rd pair that is XY, females are XX Karyotype • A visual map of all the chromsomes of a person / organism ; karyotyping is a test to examine chromosomes in a sample of cells, which can help identify genetic problems as the cause of a disorder or disease. This test can: • Count the number of chromosomes • Look for structural changes in chromosomes Punnett Square • Tool used in genetics to predict the outcome of two parents offspring ; a type of grid used to show the gametes of each parent and their possible offspring; a type of grid that can indicate all the possible outcomes of a genetic cross Pedigree • Tool used to show the passing of disorders within a family in genetics / it is an account of the descent of a person or family traced through a series of generations