* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download transcription/translation game
Catalytic triad wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
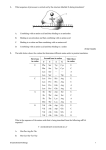
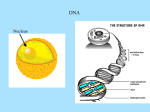
TRANSCRIPTION/TRANSLATION GAME Gene sequence: CTTGAAACTTCATAAACGGCACTGAAATAG mRNA sequence: GAACUUUGAAGUAUUUGCCGUGACUUUAUC tRNAs: cuu gaa acu uca uaa acg gca cug aaa aug Amino Acids: Leu Glu Thr Ser STOP Thr Ala Leu Lys STOP Amino Acid (1 letter): LETS_TALK_ Concept DNA transcription to messenger RNA (mRNA) and its subsequent translation into an amino acid polymer (peptide or protein). DNA is transcribed into mRNA using the A-T/G-C pairing (but substituting uracil (U) for thiamine (T)). The mRNA is then translated into a peptide sequence using transfer RNA (tRNA) that donates a particular amino acid to the chain. By using the single amino acid codes, words can be made. The Game Students are given a DNA sequence and have to go through the steps of transcription and translation in order to “decode” the secret message. Several examples can be done in small groups. Then they can try it in reverse (come up with a word and then go through the process backwards to get the DNA sequence). Students can then send their DNA sequence to another group to decode. Point out why they can’t use the letters J, O, U and X (no amino acids have these letters as their 1 letter abbreviation). Students may notice the similarity between the DNA and tRNA sequence and take the short cut. Extension You can show how mutations in DNA can “mess up” the message. They will probably have made these kinds of mistakes themselves during the game, either by misreading sequences or accidentally adding/deleting letters. Use this to discuss missense mutations (substitution of one base for another, resulting in a codon for a different amino acid), silent mutations (substitution of one base for another, resulting in a codon that codes for the same amino acid), nonsense mutations (accidental addition of a stop codon) and frameshift mutations (addition or deletion of 1 or 2 bases, resulting in a change in the reading frame). GENETIC CODE C A G G Cys Cys STOP Trp Arg Arg Arg Arg Ser Ser Arg Arg GGT GGC GGA GGG T C A G T C A G T C A G T C A G Third Position of Codon First Position of Codon T Second Position of Codon T C A Phe Ser Tyr Phe Ser Tyr Leu Ser STOP Leu Ser STOP Leu Pro His Leu Pro His Leu Pro Gln Leu Pro Gln Ile Thr Asn Ile Thr Asn Ile Thr Lys Met Thr Lys Val Ala Asp Val Ala Asp Val Ala Glu Val Ala Glu AMINO ACID ABBREVIATIONS One Letter A B C D E F G H I K L M N P Q R S T V W Y Z Three Letters Ala Asx Cys Asp Glu Phe Gly His Ile Lys Leu Met Asn Pro Gln Arg Ser Thr Val Trp Tyr Glx Amino Acid alanine asparagine or aspartate cysteine aspartate glutamate phenylalanine glycine histidine isoleucine lysine leucine methionine asparagine proline glutamine arginine serine threonine valine tryptophan tyrosine glutamine or glutamate