* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Origin of life on Earth Two approaches: • bottom-up
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
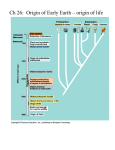
Origin of life on Earth Two approaches: • bottom-up - which of the chemical / structural parts of modern life could have formed from abiotic processes on the early Earth? • top-down - which of the constituents of current cells could have been part of earlier, simpler life forms? Basic requirements: Miller-Urey experiment 1953 experiment: mixture of several simple gases (water, hydrogen, methane and ammonia) was exposed to sparks (“lightning”) and cycled through a model of the ocean / atmosphere • genetic information (DNA) • catalytic molecules (proteins) • cell membranes (lipids) Extraterrestrial Life: Spring 2008 Result: large number of complex organic molecules formed in the experiment, including a number of amino acids Extraterrestrial Life: Spring 2008 Experiment has been repeated many times: results stand, under these conditions amino acids are synthesized easily Are the conditions a realistic depiction of the early Earth? H2O, H2, CH4 and NH3 are major constituents of the atmosphere of the giant planets. Chemically, this is a reducing atmosphere, very different from the oxidizing conditions on the Earth today. …within weeks of the discovery of the structure of DNA… Early Earth was likely devoid of oxygen, atmospheric composition would have been controlled by volcanic outgassing. Large CO2 concentration (needed for strong greenhouse effect to offset the faint young Sun) leads to less efficient synthesis of organic molecules. Extraterrestrial Life: Spring 2008 Oceanic synthesis Extraterrestrial Life: Spring 2008 Meteoritic delivery Amino acids can also be formed under conditions similar to hydrothermal vents Comets or meteorites can also be a source: Murchison meteorite may contain as many as 70 amino acids Protected against impacts, common, thermophiles seem like simple organisms… However, complex organic chemicals are also destroyed by the high temperatures - today water cycles through such systems on a timescale of only ~10 million years Extraterrestrial Life: Spring 2008 Synthesis of small molecules: site is very uncertain, but there are several plausible candidates (possibly the atmosphere, ocean vents, extraterrestrial delivery) Extraterrestrial Life: Spring 2008 1 The RNA-world hypothesis What about chirality? Currently: • DNA encodes information for building proteins • Proteins catalyze the cellular mechanisms that lead to their formation RNA (ribonucleic acid) can fulfill both functions: Both meteoritic amino acids and those synthesized in Miller-Urey type experiments tend to be almost racemic mixtures: equal amounts of left-handed and right-handed versions Additionally, the set of 20 amino acids used in biology today is not particularly favored • carry information that can be copied • can catalyze reactions, including the formation of proteins (though less efficiently than current mechanisms) Hypothesis: first life may have been based around RNA, with the DNA / protein symbiosis evolving later Extraterrestrial Life: Spring 2008 Formation of more complex molecules Getting to the RNA-world (or similar schemes based on other molecules) from simple precursors is the hardest step: Proteins alanine + glycine " di - peptide + H 2O Extraterrestrial Life: Spring 2008 Forming RNA Constituents of RNA: • sugar (ribose) • base (adenine, guanine, cytosine, uracil) • phosphate Presence of water as a product means that in water, dissociation rather than polymerization is favored… ! Moreover: more or less random order of the monomers is obtained even under conditions where proteins form Synthesis of the bases (especially adenine) appears to be relatively easy - HCN can yield adenine in water when exposed to ultraviolet light Extraterrestrial Life: Spring 2008 Sugars: pre-biotic synthesis of sugars has been demonstrated experimentally from formaldehyde (CH2O) in the presence of mineral catalysts BUT - these reactions yield a mix of many sugars (as many as 40) with no chiral preference Chirality of ribose affects the 3D structure of RNA, upon which the hereditary system rests… how did one form of ribose come to dominate? Speculation: perhaps ribose was not part of the first `RNA’-like molecules? Extraterrestrial Life: Spring 2008 Extraterrestrial Life: Spring 2008 Polymerization of nucleotides Neither of the critical steps: • reactions of the bases with ribose • reaction to join in the phosphate …have been demonstrated to occur under plausible early-Earth conditions, though there are many possible pathways. In particular, water and high temperatures are unfavorable for the survival of RNA… Where might early life have started? Extraterrestrial Life: Spring 2008 2 Role of mineral catalysts Often suggested that mineral catalysts such as clays may have played a critical role Early chemistry took place on surfaces Chirality may have been inherited from surface defects Enclosure within cell membranes came later… Extraterrestrial Life: Spring 2008 1) Organic molecules formed, either in the atmosphere, at undersea vents, or via delivery from space 2) Short strands of RNA formed with the help of catalytic materials (perhaps clays) 3) RNA became capable of self-replication 4) Membranes formed to enclose RNA 5) Natural selection led to an increase in complexity, until eventually something recognizably living formed Extraterrestrial Life: Spring 2008 Prospects for progress Clearly this topic involves too much extrapolation from `known’ conditions to allow for robust conclusions. Life started somehow - can we ever know how? • better understanding of the the atmospheres of planets (from observing others) • deeper knowledge of the function of all the molecules involved in life • lab experiments • discovery of life elsewhere Extraterrestrial Life: Spring 2008 3