* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit A Chapter 1 Lesson 1
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
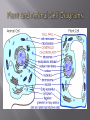
How Plant and Animal Cells Differ Pgs. A6-A11 WHAT TYPE OF THINGS HAVE CELLS IN THEM? Every living thing on this planet is made of cells. You have hundreds of trillions of cells in you . People did not know about cells until the invention of the microscope over 350 years ago. In 1665 Robert Hooke looked at slices of cork under a microscope. He was one of the first humans to observe cells. The tiny blocks he saw reminded him of the small rooms in a monastery. Because of that he named them “cells.” Can you think of a place that has very small, box-like rooms that has something to do with cells? ROBERT HOOKE SHOWING THAT REAL MEN WEAR SHIRTS WITH RUFFLES. The Cell Theory is broken into three main parts 1. 2. 3. Cells are the basic building blocks of all living things. All life activities take place in cells. Each cell carries out the activities they were designed for. New cells are produced by existing cells. Cell Membrane This thin membrane holds cell material inside and controls what enters and leaves the cell. Cell Wall (Plant Only) This stiff outer layer protects plant cells and gives it shape. It remains long after the cell dies. This is what Hooke saw in the microscope. Cytoplasm A clear, jellylike substance that fills the cells. The cells organelles float in it. Organelles are tiny structures that carry out cell activity. Mitochondria These bean shaped organelles release the energy stored in sugars to help power cell activities. You have several hundred mitochondria in each cell in your body. Ribosomes These organelles can be found floating freely in the cytoplasm. They are responsible for making proteins that your cells and body use. Somewhat mitten shaped. Golgi Apparatus This is the “delivery center” of the cell. It takes proteins made from the ribosomes and modifying them, making them stronger. It then packages the proteins and sends them to the rest of the cell and outside as well. It resembles a stack of deflated balloons. Chloroplast (Plant Only) The chloroplast in plant cells allow plants to make their own food. This process is called photosynthesis. Vacuole This is a storage space inside of cells. Food, water, and waste are stored here. Think of the plastic tubs you might use to store things in. Nucleus This is the control center of the cell and directs all of the cell’s activities. It contains the chromosomes inside of it. Chromosome These contain the information (DNA) that determines the characteristics of the organism. Nuclear Membrane This membrane surrounds the nucleus and holds it together. Animal and Plant Cells Game