* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
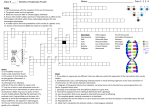
Genetics Vocabulary List Alleles: Alternative forms of a trait. Autosomes: All chromosomes with the exception of the sex chromosomes. Biology: The study of life. Carrier: An individual who has the allele for a trait or disease but does not have the disease or outwardly express the trait. Diploid: A cell that contains both chromosomes of a homologous pair . A set from each parent (body cells). Dominant Allele: Masks the recessive allele in a heterozygous individual. Gamete: Reproductive cell. This would be the egg or sperm Gene: Section of a chromosome (DNA) that codes for a specific trait. Genetics: Field of Biology devoted to understanding how traits are inherited through generations. Genome: The complete genetic material contained in an individual. Genotype: The genetic make-up of an organism. Gregor Mendel: Father of genetics. He studied traits in pea plants. Haploid: A cell that contains one set of chromosomes (gametes). Heterozygous: Genotype of an individual with two different alleles for a given trait. Homologous Chromosomes: The pairs of chromosomes in a diploid individual that have the same overall genetic content (matching). One member of each homologous pair of chromosomes in inherited from each parent. Homozygous: Genotype of an individual with two of the same alleles for a given trait. Incomplete Dominance: Occurs when neither allele is dominant. They both have an affect on the heterozygous individual which shows a phenotype between the two homozygous phenotypes. Law of Dominance: If two alleles in a gene pair are different, then one allele can control and the other can be hidden. Law of Independent Assortment: Alleles for a trait separate randomly and independently of each other. Pedigree: A diagram of the genetic history of an individual: can show how a trait is inherited over several generations of a family. (A genetic family tree) Phenotype: The external appearance of an individual determined by it’s genotype. Punnett Square: A model used to show the probabilities of the results of a genetic cross. Recessive Allele: Allele that is masked by the dominant allele in a heterozygous individual Sex Chromosomes: The pair of chromosomes that determine the gender of an individual. Somatic cell: Body cell such as skin cell, muscle cell, etc The Law of Segregation: Each pair of alleles segregates (separates) during gamete formation. Each gamete contains one allele from each pair. Trait: Any characteristic that can be passed be inherited from parent to offspring. Alleles: Alternative forms of a trait. Autosomes: All chromosomes with the exception of the sex chromosomes. Carrier: An individual who has the allele for a trait or disease but does not have the disease or outwardly express the trait. Diploid: A cell that contains both chromosomes of a homologous pair. A set from each parent (body cells). Dominant Allele: Masks the recessive allele in a heterozygous individual. Gamete: Reproductive cell. This is the egg or sperm Gene: Section of a chromosome (DNA) thatcodes for a specific trait. Genetics: Field of Biology devoted to understanding how traits are inherited through generations. Genome: The complete genetic material contained in an individual. Genotype: The genetic make-up of an organism. Gregor Mendel: Father of genetics. He studied traits in pea plants. Haploid: A cell that contains one set of chromosomes (gametes). Heterozygous: Genotype of an individual with two different alleles for a given trait. Homologous Chromosomes: The pairs of chromosomes in a diploid individual that have the same overall genetic content (matching). One member of each homologous pair of chromosomes is inherited from each parent. Homozygous: Genotype of an individual with two of the same alleles for a given trait. Incomplete Dominance: Occurs when neither allele is dominant. They both have an effect on the heterozygous individual which shows a phenotype between the two homozygous phenotypes. Law of Dominance: If two alleles in a gene pair are different, then one allele can control and the other can be hidden. Law of Independent Assortment: Alleles for a trait separate randomly and independently of each other. Pedigree: A diagram of the genetic history of an individual: can show how a trait is inherited over several generations of a family. Phenotype: The external appearance of an individual determined by it’s genotype. Punnett Square: A model used to show the probabilities of the results of a genetic cross. Recessive Allele: Allele that is masked by the dominant allele in a heterozygous individual Sex Chromosomes: The pair of chromosomes that determine the gender of an individual. Somatic cell: Body cell such as skin cell, muscle cell, etc The Law of Segregation: Each pair of alleles segregates (separates) during gamete formation. Each gamete contains one allele from each pair. Trait: Any characteristic that can be passed be inherited from parent to offspring.