* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Immunity II
Gluten immunochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Herd immunity wikipedia , lookup
Complement system wikipedia , lookup
Social immunity wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Plant disease resistance wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Anti-nuclear antibody wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
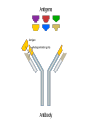
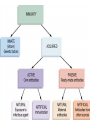
Do Now: List and describes the immune response Primarily involve White Blood Cells (WBC’s) a. Phagocytes: engulf or ingest foreign invaders b. Lymphocytes: more specific in targeting invaders 1. b cells: creates antibodies 2. helper T cells: coordinates response 3. T cells: kill infected cells 1. Recognition Lymphocytes White blood cells called _______________ “patrol” the blood looking for pathogens. Pathogens are recognized/identified by their surface structures called ________________ antigens 2. Antibody Production Once the pathogen is identified antibodies are produced which attach to the antigens on the pathogen to spreading of pathogen prevent__________________ Antibodies are produced by the B-cells 3. Destruction of Pathogen Once surrounded by antibodies the T-cells/Killer T-cells destroy the pathogen by engulfing it Phagocytosis through the process of ___________________ 4. Memory Memory B cells “remember” the antibodies needed to fight this particular pathogen in case of future invasion Immunity that you gain during your life time Immunity that your are born with due to genetics factors in your DNA When you produce your own antibodies Natural: When you are exposed to the pathogen and you body make the necessary antibodies Artificial: When you are Immunized which prompts your body to produce the antibodies When you receive ready-made antibodies Natural: When you receive maternal antibodies from _________________________ breast milk during infancy Artificial: When you receive antibodies from another source usually through antibiotics ________________ The process in which an individual gains immunity against a specific pathogen due to the injection of a vaccine A solution that contains a weakened form of a specific pathogen or dead form of a specific pathogen that is injected into the bloodstream to prompt an immune response Do Now: Describe how the flu vaccine protects the human body. In your answer be sure to: • Identify the substance in the flu vaccine that stimulates immunity (1) • State how the human immune system reacts to the vaccine (1) • State one reason the flu vaccine does not protect from viral diseases such as measles. (1) 1) A.I.D.S: • Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome is caused by HIV. • Human Immune Virus – the virus attacks the Killer T-cells, causing the body to be unable to fight disease. • Once infected, a person can be reinfected with a different strain • when the immune system causes an overreaction to an antigen • Results: increase production of histamines, which causes discomfort. • Histamines increase blood flow and fluids to surrounding areas causing sneezing, runny nose and other irritations. • Treatment - Antihistamines When the body goes through the immune response process and “recognizes” a pathogen (the new organ), resulting in immune action. Results – the organ is destroyed by the person’s immune system Prevention • organ recipient is given immunosuppressant drugs. Side effects of immunosuppressant drugs: Person is vulnerable to other diseases due to lack of functioning immune system. When the body is unable to distinguish “itself”. Body actually begins to attack itself, causing damage to tissues leading to other malfunctions. a. Multiple Sclerosis b. Lupus c. Juvenile diabetes d. Arthritis e. Cancer The presence of parasites in an animal will usually result in 1. an increase in meiotic activity within structures of the host 2. the inability of the host to maintain homeostasis 3. the death of the host organism within twenty-four hours 4. an increase in genetic mutation rate in the