* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Molecular and Clinical Markers for the Diagnosis and Treatment of
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Birth defect wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Tay–Sachs disease wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Fetal origins hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
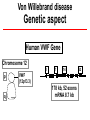
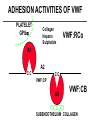
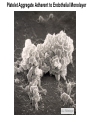
Molecular Genetics in the Von Willebrand disease Ghasem Rastegarlari VON WILLEBRAND DISEASE VWD General definitions • The most frequent congenital bleeding disorder caused by defects of VWF: - quantitative = Types 1 & 3 VWD - qualitative = Type 2 VWD • Autosomal dominant/recessive pattern • Women are more symptomatic Von Willebrand disease Genetic aspect Human VWF Gene Chromosome 12 1 p q 7 14 VWF (12p13.3) 178 kb, 52 exons mRNA 8.7 kb 52 ENCODING REGIONS OF VWF AND FUNCTIONAL DOMAINS VWF gene in Chromosome 12 5’ bp 0 3’ 1000 2000 1-23 H2N 3000 D2 5000 6000 7000 8000 Multimers S-S 163 D1 4000 D’ FVIII D3 Dimers S-S A1 A2 A3 Platelets Endothelial cells D4 9000 2813 C1 C2 CK COOH B1 B2 B3 RGD IIb3 ADHESION ACTIVITIES OF VWF PLATELET GPIb Collagen Heparin Sulphatide VWF:RCo A1 A2 CC CC VWF:CP A3 A3 VWF:CB SUBENDOTHELIUM COLLAGEN Single Platelets Adherent to Endothelial Monolayer 6 A.J. Reininger Platelet Aggregate Adherent to Endothelial Monolayer A.J. Reininger 7 MOLECULAR MARKERS of Type 3 VWD • Complete deficiency of VWF (VWF:Ag < 1) • Autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance • Rare (1- 5 per million) but severe disorder •Caused by several defects: gene deletions, frameshift-nonsense-missense-splite site mutations, defects of mRNA expression CLINICAL & MOLECULAR MARKERS of Type 2 VWD • Type 2A, 2B and 2M variants with decreased platelet-dependent function Autosomal dominant • Can be caused mainly by missense mutations (small deletions or frameshift mutations also) CLINICAL & MOLECULAR MARKERS of Type 2N VWD • Variants with markedly decreased affinity for factor VIII (FVIII) • Inherited by recessive patterns •Caused by missense mutations CLINICAL & MOLECULAR MARKERS Type 1 VWD • Inheritance (autosomal dominant) •BUT: Factors which can modify VWF levels: • Sex (females may exhibit greater variability) • Age (VWF higher in older individuals) • Exercise and stress (VWF increases) • Blood Group O (lower VWF levels) Von Willebrand disease Genetic aspect It is important to determine the causative defect of VWF gene: to prove phenotypic diagnosis or to make a definite diagnosis of VWD when the phenotypic diagnosis is uncertain, Prenatal diagnosis Direct sequencing of the VWF gene Conclusion (1) We have investigated 121 unrelated VWD patients 66 unrelated type 2 VWD patients 50 unrelated type 3 VWD B patients The molecular defects have been found in 109 patients with a detection rate of ~ 90% Nineteen novel mutations (not previously reported, in the International VWD mutation databases). Conclusion (2) Identified mutations in VWD patients allowed direct carrier diagnosis and prenatal diagnosis Mutation analysis is now routinely carried out and is used as a first line method for carrier detection and will be used for prenatal diagnosis. All molecular analysis from the DNA extraction to sequencing were done in our Iranian Comprehensive Hemophilia Treatment Center