* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant Hormones
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
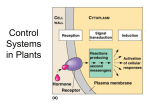
Biotechnology II What is a plant hormone? How are plant hormones are involved in the plant’s signal transduction mechanism? Compound produced by one part of an organism that is transported to other parts where it triggers a response in target cells and tissues Considered to be a chemical signal that stimulates/inhibits biological response(s) Growth and development by controlling Division Elongation Cell differentiation Involves four stages: Signal- environmental or chemical Reception- signal detection; commonly, on cell membrane Transduction – amplification of the signal within the cell Cellular Response – ▪ gene expression- turning on/off transcription ▪ changes in enzyme activity- more active/less active Chemical – hormones, nutrients (e.g. glucose) Effect of hormone Gibberellic Acid on Internode elongation in plants Present in low concentration (10-10M) Differ in where they are made and their mode of delivery Detect by the presence of receptor Receptor has a binding site complementary to signaling molecule, often referred to as a ligand Binding of the signal generally causes the receptor protein to change in shape Triggers the production of secondary messengers, which amplify the signal Allows large biological response Stimulate seed germination Inhibit seed germination Promote cell elongation Promote fruit ripening Phototropism – bending towards the light Came from series of classic experiments studying phototropism Plant used for these studies: grass seedlings, specifically oats Charles Darwin and son, Francis (1880)- observed that the tip of coleoptile was required to bend towards light Boysen-Jensen’s Experiment (1913) – showed that the signal was a chemical passing down from the coleoptile tip F. W. Went (1926) – extracted the growth stimulus. Amount of auxin in coleoptile tips too small to purify; Went developed bioassay to determine relative amounts Determined that the degree of curvature was proportional to amount of auxin activity Auxin (IAA) Cytokinins (zeatin) Gibberellins (GA3) Abscisic Acid Ethylene Apical meristem major site of auxin production Stimulates cell growth at low concentrations 10-8 to 10-3 M Moves from apex (tip of plant) to zone of elongation at a rate of 10 mm per hr. In region of elongation, proton pump pumps H+ into cell wall. Result: Lowers pH of cell wall Acidification activates enzymes called expansins break crosslinks in cell wall Change in pH causes ion (charged elements) uptake; Drives uptake of water and cell elongation Analogous to blowing up a balloon Induce fruit production without pollination Promote growth of roots Inhibits loss of leaves Several companies produce a synthetic form of auxin – 1-napthaleneacetamide Active ingredient in many commercial rooting compounds Cytokinin Promote cell division Prevents senescence Used commercially to prolong the shelf life of flowers and vegetables Types of organs that form depends on ratio of auxin to cytokinin concentration Auxin > Cytokinin ▪ Rooting on Callus Auxin = Cytokinin ▪ Callus formation Auxin < Cytokinin ▪ Axillary bud development Gibberellin Promotes stem elongation Used commercially ▪ to increase growth and size of plants ▪ Break seed dormancy Abscisic Acid Initiates and maintains seed and bud dormancy Used commercially for thinning of fruits ▪ Promote growth of remaining fruit + GA -GA Ethylene Involved in abscission and ripening of fruit Used commercially to ▪ Ripen fruit and vegetables for market What four stages are involved in plant signal transduction mechanism? Explain how hormones stimulate biological response? Which hormones would produce an in increase in the size of plant’s organs Explain why abscisic acid is sometimes referred to as an inhibitory hormone.