* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Aerobic Respiration
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
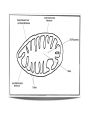
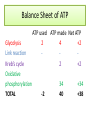
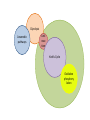
Aerobic Respiration In summary, aerobic respiration is: • Glycolysis – the phosphorylation of glucose to 6C hexose phosphate, then splitting into 2 x 3C triose phosphate molecules which are oxidised to form 2 x pyruvate, yielding a little ATP and reduced NAD. In cytoplasm. • Link reaction - pyruvate is decarboxylated and hydrogenated. The remaining 2C unit is added to CoA to form AcetylCoA. This occurs twice for every glucose molecule as 2 x pyruvate are formed. In mitochondria. Acetyl Coenzyme A • A complex organic molecule containing a nucleotide (adenine and ribose) with a B group vitamin (pantothenic acid) • Acts as a carrier of acetyl groups to the Kreb’s cycle • Acetyl CoA (2C) then combines with oxaloacetate (4C)to form citrate (6C) which then enters the Kreb’s cycle in mitochondria. • During the Kreb’s cycle, citrate is reconverted to oxaloacetate in a series of small steps. • These processes involve decarboxylation and dehydrogenation, using NAD and FAD as hydrogen carriers. • For each turn of the cycle 2 CO2 molecules are produced, one FAD and 3 NAD are reduced, and one ATP generated. • Finally, oxidative phosphorylation occurs, converting ADP to ATP using energy from the activity of electrons in the electron transfer chain (ETC). Also in mitochondria. • Reduced NAD and FAD are passed to the ETC where hydrogen is removed and split into H+ and an electron. • The electron is transferred to the first electron carrier, whilst H+ remains in solution. • As the electron is transferred to oxygen, H+ is drawn from solution to reduce oxygen to water. • The transfer of electrons makes energy available to convert ADP + Pi to ATP. • As an electron passes from a carrier at a higher level to one at a lower level, energy is released. • This energy is usually lost as heat but at particular points in the ETC it is enough to produce ATP. • 3xATP produced for each reduced NAD. • 2xATP produced for each reduced FAD. Balance Sheet of ATP Glycolysis Link reaction Kreb’s cycle Oxidative phosphorylation TOTAL ATP used ATP made Net ATP 2 4 +2 2 +2 -2 34 40 +34 +38 Glycolysis Anaerobic pathways Link reac tion Kreb’s Cycle Oxidative phosphory lation Chemiosmosis Chemiosmosis is the most likely explaination for the synthesis of ATP in oxidative phosphorylation. Energy released by ETC is used to pump hydrogen ions into the space between the two membranes of the mitochondrial envelope. Concentration of H+ in intermembrane space > concentration of H+ in mitochondrial matrix. H+ ions pass back into mitochondrial matrix through protein channels in inner membrane. ATP synthetase associated with channels. As H+ passes through, their electrical potential energy is used to synthesise ATP from ADP +Pi.