* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Protein Structure
Protein design wikipedia , lookup
Rosetta@home wikipedia , lookup
Bimolecular fluorescence complementation wikipedia , lookup
Structural alignment wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Homology modeling wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Protein domain wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein folding wikipedia , lookup
Protein mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
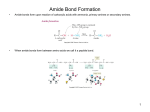
Protein Structure Biochemistry Free For All From Amino Acids to Proteins Peptide Bonds In Ribosomes Alpha Carboxyl Alpha Amine Primary Protein Structure • • • • Linear sequence of amino acids Joined by Peptide Bonds Translated from mRNA using Genetic Code Synthesis begins at amino end and terminates at carboxyl end • Ultimately determines all properties of a protein Polypeptides Alternating Orientations of R-groups A simple view Peptide Bond Peptide Bond Free Carboxyl Group Peptide Bond Amino Terminus Carboxyl Terminus Peptide Bond Peptide Bond Free Alpha Amine Alternating Orientations of R-groups Peptide Bonds Chemical Character Double Bond Behavior Alpha Carbons Usually Trans-oriented Proteins Alpha Carbons Trans Steric Hindrance Separated bulky groups Interacting Bulky Groups Alpha Carbons Cis Separated bulky groups Polypeptides Multiple Peptide Bond Planes Free Rotation Phi and Psi Angles Psi Angle Phi Angle Peptide Bond Peptide Bond Omega Angle Ramachandran Plot Bond Angles Primary Angles of Stability Secondary Structure Alpha Helix Secondary Structure Alpha Helix Hydrogen bonds stabilize structure Hydrogen bonds stabilize structure Secondary Structure Hydrogen Bonds Beta Strands / Beta Sheets Anti-Parallel Parallel Beta-Sheet Interactions Secondary / Supersecondary Structures Ramachandran Plot Labeled Secondary Structure Fibrous Proteins • Collagen • Connective tissue • Keratin • Hair / nails • Fibroin • Silk Collagen Primary Structure Hydroxyproline Proline in Helix Abundant Glycine Occasional Lysine Partial Sequence Structural Proteins Keratins Fibrous 50 in Humans Intermediate Filaments of Cytoskeleton Hair, nails, horns Fibroin Silk Beta sheets Repeating glycines Secondary Structure Types Alpha Helix Beta Strands / Beta Helix Reverse turns (5 types) 310 Helix Secondary Structure Tendencies of Amino Acids High Propensity for Alpha Helices High Propensity for Reverse Turns High Propensity for Beta Strands Amino Acid Hydropathy Soluble vs. Membrane Bound Proteins Hydrophobic Amino Acid Bias Inside Hydrophilic Amino Acid Bias Outside Hydrophobic Amino Acid Bias In Bilayer Hydrophilic Amino Acid Bias Outside of Bilayer Reverse Turns Tertiary Structure Folding and Turns Beta Strands Alpha Helices Random Coil Turns Folding of a Globular Protein Unfolding of a Globular Protein Forces Stabilizing Tertiary Structure Hydrogen Bonds Forces Stabilizing Tertiary Structure Disulfide Bonds (Covalent) Forces Stabilizing Tertiary Structure Denaturing/Unfolding Proteins Break forces stabilizing them Mercaptoethanol/dithiothreitol - break disulfide bonds Detergent - disrupt hydrophobic interactions Heat - break hydrogen bonds pH - change charge/alter ionic interactions Chelators - bind metal ions Denaturing/Unfolding Proteins Folding of a Globular Protein Energetics of Folding Protein Structural Domains Leucine Zipper - Prot.-Prot. and Prot.-DNA Helix Turn Helix - Protein-DNA Leucine Zipper Zinc Fingers SH2 Domains - Protein-Protein Pleckstrin Homology Domains - Signaling (Membrane) Leucine Zipper Zinc Finger Helix-Turn-Helix SH2 Domain Pleckstrin Domains Folding Errors Prion Replication Model Amyloids and Disease Amyloids - a collection of improperly folded protein aggregates found in the human body. When misfolded, they are insoluble and contribute to some twenty human diseases including important neurological ones involving prions. Amyloid diseases include (affected protein in parentheses) - • Alzheimer’s disease (Amyloid β) • Parkinson’s disease (α-synuclein) • Huntington’s disease (huntingtin), • Rheumatoid arthritis (serum amyloid A), • Fatal familial insomnia (PrPSc) Protein Processing Chaperonins - Proper folding - environment for hydrophobic sequences GroEL / GroEL-GroES Proteasomes - Degradation to oligopeptides of about 8 amino acids each Role of Ubiquitin Flag for protein destruction by proteasome Intrinsically Disordered Proteins Not all proteins folded into stable structures Intrinsically Disordered Proteins (IDPs) have regions favoring disorder IDP regions tend to lack hydrophobic residues Rich in polar amino acids and proline IDPs may favor adaptation to binding another protein IDPs may favor being modified IDPs may be more involved in signaling and regulation Non-IDPs more involved in catalysis and transport Metamorphic Proteins May adopt more than one stable structure Lymphotactin - monomeric receptor. Binds heparin as dimer Protein Structure • Primary – Amino Acid Sequence • Secondary / Supersecondary – Repeating Structures – short range forces • Tertiary – Folded structures – longer range interactions