* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Meeting Time/Place - Penn State Meteorology
Heaven and Earth (book) wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit email controversy wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Soon and Baliunas controversy wikipedia , lookup
ExxonMobil climate change controversy wikipedia , lookup
Numerical weather prediction wikipedia , lookup
Climate change denial wikipedia , lookup
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
Climate resilience wikipedia , lookup
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
Climate change adaptation wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Global warming hiatus wikipedia , lookup
German Climate Action Plan 2050 wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Instrumental temperature record wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric model wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit documents wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Michael E. Mann wikipedia , lookup
Climate engineering wikipedia , lookup
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on Australia wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
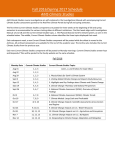
Climate Dynamics (METEO 470, 3 credits) Course Syllabus for Spring 2014 Instructor: Michael E. Mann, Department of Meteorology, 514 Walker Building, [email protected] Teaching Assistant: Sreece Goldberger, Department of Meteorology, 418 Walker Building, [email protected] Meeting Time/Place: TuTh 1:00-2:15P (103 Walker) Office Hours: You are encouraged to use email for questions when possible. You are welcome to visit my office for questions during scheduled office hours (Wed 1:00-2:15 PM), or by appointment. Motivation: In order to under and model the climate system, we need to understand the dynamics of the underlying components, including the atmosphere and ocean, and the mechanisms by which they are coupled. In this course, we will model the dynamics and thermodynamics governing the ocean and atmosphere on spatial and temporal scales appropriate for climate studies. We will investigate the processes by which the dynamics of the ocean and atmosphere are coupled on these timescales, with the goal of understanding the basic mechanisms of climate variability. Topics discussed will include the thermohaline and wind-driven ocean circulation, energy balance, the El Nino/Southern Oscillation (ENSO), internal and forced climate variability, and climate change. Webpage We will regularly draw upon the course homepage as a resource for the course: http://www.meteo.psu.edu/~mann/Mann/courses/METEO4 70SPR14/index.html Aside from links to the course syllabus, there will be links to the readings, problem sets, slides from the lectures, and other course-related materials. Lectures Attendance of all lectures is expected. You are strongly encouraged to ask questions and participate constructively in class. Copies of slides from the lectures will usually be made available electronically through the course website (see above) within 2-3 days following the lecture. Textbook There is no required textbook. I recommend as a reference: Peixoto and Oort (1992), Physics of Climate, 2nd Edition, American Institute of Physics Press, 564pp. (suggested readings indicated in lecture schedule below). Where appropriate, supplementary readings taken from various sources will be posted on the course website. Grading Problem Sets (40%): There will be several (4) problem sets assigned that will involve applications of topics covered in class. You may discuss the problems with each other, but the problem set you turn in should reflect your own individual effort. “Up In the Air” Project (10%): You will participate in a project (in teams of 2-3 students) aimed at producing content (related to some aspect of the course) for use in the Meteorology Department’s new “Up In the Air” Television program. Projects are **DUE MARCH 21**. Each project team will give a short presentation sometime after Spring Break (mid March through mid April). Mid-Term Exam (20%): There will be a mid-term examination roughly mid-way through the semester. Final Exam (30%): There will a final examination for the course at the scheduled time and date. LECTURE SCHEDULE (tentative and subject to change) 1 2 DATE T Jan 14 R Jan 16 T Jan LECTURE TOPIC Introduction READING 1; 2 ASSIGNMENT “Up in the Air” workshop [Media Commons, W140 Pattee Library] Math & Stat review; Equations 3.1-3.2.1 PS #1 Assigned 6 21 R Jan 23 T Jan 28 R Jan 30 T Feb 4 7 R Feb 6 8 T Feb 11 R Feb 13 T Feb 18 R Feb 20 T Feb 25 R Feb 27 T Mar 4 R Mar 6 T Mar 11 R Mar 13 T Mar 18 R Mar 20 T Mar 25 R Mar 27 T Apr 1 3 4 5 G1 9 G2 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 G3 R Apr 3 T Apr 8 G4 R Apr of Motion Equations of Motion (cont) Energy Equation 3.4.1 Equation of State (for Atmosphere) Filtering of Governing Equations (for Atmosphere) Large-Scale Atmospheric Circulation Large-Scale Atmospheric Circulation (continued) Guest Lecture: Ice Sheet Dynamics (David Pollard) Hydrological cycle; Salinity; Equation of State for Ocean Guest Lecture: Tracers of Ocean Circulation (Ray Najjar) Filtering of Governing Equations (for Ocean) Mid-term 3.5;3.5.1 Large-scale Ocean Circulation— Ekman transport Large-scale Ocean Circulation— Ekman circulation No Class [Spring Break] 3.2.3;8 3.2.2 PS #1 Due 3.2.2; 7 PS #2 Assigned 3.5.2;12;12.1.112.5.2 PS #2 Due 3.2.3 No Class [Spring Break] Large-scale Ocean Circulation— Sverdrup transport Large-scale Ocean Circulation— gyre circulation Large-scale Ocean Circulation— thermohaline circulation (THC) Climate Modeling: Energy Balance Models Climate Modeling: Energy Balance Models (cont) Climate Modeling: Energy Balance Models (cont) Guest Lecture: Early Earth Climate Evolution (Jim Kasting) Guest Lecture: Paleoclimatology PS #3 Assigned 6-6.3; 6.6-6.8; 10-10.7 Supplemental Readings Supplemental Readings PS #3 Due PS #4 Assigned 20 G5 21 22 23 24 10 T Apr 15 R Apr 17 T Apr 22 R Apr 24 T Apr 29 R May 1 (Byron Steinman) Climate Modeling: El Nino/Southern Oscillation Guest Lecture: Proxy Records of El Nino (Byron Steinman) Climate Modeling: El Nino/Southern Oscillation (cont) Climate Modeling: Coupled Ocean-Atmosphere Models Climate Modeling: Coupled Ocean-Atmosphere Models Anthropogenic Climate Change Supplemental Readings Supplemental Readings Supplemental Readings PS #4 Due