* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Making sense of the vast Diversity of Life
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
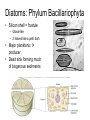
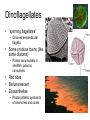
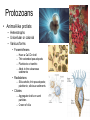
Organizing the diversity • Systematics; studying the diversity – Taxonomy to classify organisms & groups • Prokaryotic – – – – – Bacteria and bacteria-like Simpler Smaller cell size DNA without nucleus Cell wall & other crude protective layers – Lack organelles • Eukaryotic – Protista, Plants, Fungi, & Animals – Complex – >cell size; 10x larger – DNA in nucleus – Cell membrane • Some also have cell wall – Membrane bound organelles • specialization • Domains Bacteria & Archaea Domain Eukarya Bacteria • Morphology – Rods (bacilli) – Spheres (cocci) – Spirals • Feeding – Heterotrophic – Autotrophic • Photoautotrophic • Chemoautotrophic • Oxygen pathways – Aerobic – Anaerobic – Facultative anaerobic • Decomposers – Breakdown DOM – Ammonia → nitrate – N2 gas → NH4 → nitrate Archaea • Similar in shape and simplicity to Bacteria – Share some genetic similarities with Eukaryotes • Extremophiles – – – – Temperature (>/= 121o) Salinity pH e.g. hydrothermal vents Other fun marine microbes • Unicellular algae – Plant-like Protists – Mostly photosynthetic • Autotrophs converting light E to ATP – Primary producers – Planktonic • Drift in the water column Diatoms: Phylum Bacillariophyta • Silicon shell = frustule – Glass-like – 2 halves like a petri dish • Major planktonic 1o producer • Dead sink forming much of biogenous sediments Diatom reproduction Dinoflagellates • “spinning flagellates” – Grooved perpendicular flagella • Some produce toxins (like some diatoms) – Poison accumulates in shellfish; poisons consumers • Red tides • Bioluminescent • Zooxanthellae – Photosynthetic symbionts of anemones and corals • Chrysophyta – Silicoflagellates • Star shaped; silicon – Desmids • Pectin & silican walls • Golden or yellow • Coccolithorids – Calcium carbonate coccoliths • All are important planktonic 1o producers Emiliania huxleyi (E. huxleyi) Protozoans • Animal-like protists – Heterotrophs – Unicellular or colonial – Various forms • Foraminiferans – – – – Have a CaCO3 shell Thin extended pseudopods Planktonic or benthic Adds to the calcareous sediments • Radiolarians – Silica shells; thin pseudopods; planktonic; silicious sediments • Ciliates – Aggregate shells or sand particles – Crown of cilia Fungi • Heterotrophic – Decomposers • Breakdown DOM – Some parasitic – Some symbiotic • w/ algae &/or cyanobacteria • = Lichens • Fungi provide structure & support (home); algae provides photosynthesis products (sugars)