* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AMP-activated protein kinase induces apoptosis in LX2 cell
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Protein phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
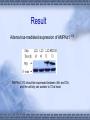
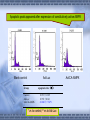
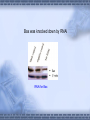
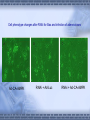
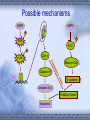
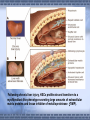
AMP-activated protein kinase induces apoptosis in LX2 cells involving of Bax pathway Background Result Possible mechanism Next works Background Hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) are a major fibrogenic cell type which contributes to extracellular matrix accumulation during chronic liver diseases. HSCs also play a critical role in the resolution of hepatic fibrosis, where activated HSCs take place apoptosis. So inducing apotosis of HSCs is a potential therapic strategy for hepatic fibrosis. Recent evidence has indicated that AMPactivated protein kinase (AMPK) can induce apoptosis of several kinds of cells, such as rat liver cells, MIN6 cells and human neuroblastoma cells, but little is known regarding this matter in HSCs. AMPK AMPK is a serine/threonine protein kinase, composed of a catalytic subunit (α) and two regulatory subunits (βandγ) . AMPKα1 1-312 residues no longer associates with theβandγsubunits but retaines significant kinase activity . Mutation of thronine 172 within theαsubunit to an asparitic acid residue within this truncated protein prevent its inactivation by protein phosphatases. Result Adenovirus-mediated expression of AMPKα1 312 AMPKα1 312 should be expressed between 48h and 72h, and the activity can sustain to 72 at least. Expression of constitutively active AMPK induces apoptosis in LX2 cell DNA ladder appeared after expression of constitutively active AMPK Lane1: Marker Lane2: treated with Ad-CA-AMPK Lane3: treated with Ad-Luc Lane4: treated with H2O2 Lane5: blank control Apoptotic peak appeared after expression of constitutively active AMPK Blank control Ad-Luc Group Control Ad-Luc Ad-CA-AMPK apoptosis rate(%) 0.873±0.389 0.953±0.141 26.040±7.762*# * vs to control; # vs to Ad-Luc Ad-CA-AMPK Bax was up-regulated with the over-expression of AMPK Bcl-2 is expressed at a low level Pro-caspase-3 was activated and bax was upregulated Bax was knocked down by RNAi RNAi for Bax Cell phenotype changes after RNAi for Bax and infection of adenoviruses Ad-CA-AMPK RNAi + Ad-Luc RNAi + Ad-CA-AMPK Activation of caspase-3 induced by AMPK recovered with RNAi for Bax Possible mechanisms AMPK AMPK P P JNK ACC P c-Jun Cyto c Malonyl-CoA Caspase-9 ba x β-oxidation Caspase-3,6,7 Oxidative stress Apoptosis 下步的工作 进一步证实AMPK是不是通过JNK通路激活了Bax,诱导凋 亡。 动物试验 1. 建模后尾静脉注射Ad-CA-AMPK, 2. Metformin,TZDs喂食动物,分析其对肝纤维化的影响。 调查,统计分析: Metformin, TZDs在治疗糖尿病患者时是 否对与同时患有肝炎的人同样具有治疗作用。 Thank you! Metformin:二甲双胍, 通过抑制糖原异生及糖原 的分解,可降低糖尿病时 的高肝糖生成率。 TZDs:噻唑烷二酮,也 称格列酮类药物,增强靶 组织对胰岛素的敏感性。 其中TRG(曲格列酮)可 引起肝损伤,同类药物还 有RSG(罗格列酮), PIO(帕格列酮)。 Following chronic liver injury, HSCs proliferate and transform to a myofibroblast-like phenotype secreting large amounts of extracellular matrix proteins and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase(TIMP). Consequences of hepatic AMPK activation. The pharmacologic agents, metformin and thiazolidinediones (TZDs), activate AMPK in the liver. In addition, the deletion of SCD results in AMPK activation through an undetermined mechanism. The activation of AMPK reduceslipogenesis through three independent mechanisms. Activated AMPK phosphorylates and inhibits the activity of ACC, which reduces malonyl-CoA formation. ChREBP is phosphorylated by activated AMPK, which inhibits its entry into the nucleus, thus suppressing L-PK and lipogenic gene expression. SREBP-1c expression is reduced by activated AMPK through undefined mechanisms. The cumulative result of AMPK activation, whether by drugs or through the deletion of SCD, is a reduction in fatty acid synthesis, decreased malonyl-CoA concentrations, and increased CPT-1 activity, resulting in increased fatty acid oxidation.