* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download floor features notes
Atlantic Ocean wikipedia , lookup
History of research ships wikipedia , lookup
Demersal fish wikipedia , lookup
Southern Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Marine pollution wikipedia , lookup
Marine biology wikipedia , lookup
Pacific Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem of the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Indian Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Arctic Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
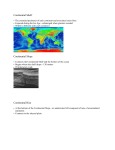
The Ocean Floor and Its Sediments Chapter 16 Ocean Floor Features • Divided into 2 main regions –Continental margins –Ocean basins Continental Margins • Continental Shelves: – Part of the continent that is underwater •Extends from the shoreline to the “shelf edge” Continental Margins • Continental slopes – Begin at the shelf edge – Where water depth starts to increase rapidly – Crust changes from continental to oceanic Continental Margins • Active Continental Margins – Shelf is narrow and bordered by an ocean trench – Shoreline is rugged with coastal mountains – Plate boundaries Continental Margins • Passive continental margins – Shelf is broad – No bordering trench or coastal mountains – Continental rises are only found at passive margins – No plate boundaries Continental Margins • Submarine canyons – Start on continental shelf – Continue all the way to the end of the slope – Sometimes formed by rivers emptying into the ocean Continental Margins • Turbidity Currents – “turbid” means muddy – Powerful currents that run like flash floods down the continental slopes – Form when landslides of mud and sand come down the slopes – Erosion! – Build fan-shaped deposits at the mouths of the canyons (abyssal fans) Continental Margins • Continental Rise – Gently sloping region between continental slope and ocean basin – Formed by deposition of sediment from land brought by turbidity currents – Not found at active continental margins Ocean Basins • Abyssal Plains –Flattest areas of Earth’s surface –Made of sediment from continents –Common in Atlantic Ocean Ocean Basins • Seamounts – Cone-shaped mountain peaks that rise high above the deep ocean floor – Often found in clusters or rows near plate boundaries – Most abundant in Pacific – Volcanic origins Ocean Basins • Guyots (GHEE-ohs) –Flat topped seamounts –Thought to have been above water, where waves eroded the tops –Then crust sank, and guyots are now underwater Ocean Basins • Atolls – Ring-shaped coral islands – Reef forms around volcanic island – Sea floor sinks, and mountain drops lower – New coral grows on top of old coral, so eventually the mountain is underwater with the ring of coral around where it used to be – Lagoon in the center