* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Variation
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Copy-number variation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
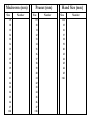
Variation What is variation? Variation Lab – Day 1 Variation Lab – Day 2 How does variation arise? Variation - a difference or deviation in structure or character from others of the same species or group Single-gene Traits – traits controlled by a single gene that has two alleles Examples – cleft chin, hitchhiker’s thumb, tongue rolling, attached/unattached earlobes Polygenic Traits– traits controlled by two or more genes Range of phenotypes More than two genes Examples – height, performance on IQ tests, skin color, eye color Variation Lab – Definitions Species - a group of organisms capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring Population – groups of individuals of the same species that interbreed Gene Pool – all genes that are present in a population Variation Lab – What will you be doing? Mealworms – LENGTH of mealworm (mm) Peanuts – LENGTH of inside nut, or cotyledon (mm) Hand – LENGTH of hand spread from thumb to little finger Variation Lab - Predictions Variation Lab - Graphing Variation Lab – Graphing Instructions Label the x-axis (independent variable) and the y-axis (relative frequency). Determine the maximum and minimum values for each variable and a standard width for each bar and set them on your axes. Draw a bar for each range of values that shows how many organisms have a trait that measures within that range. Repeat this for all ranges of measurements. Mealworm (mm) Size <9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 >28 Number Peanut (mm) Size <9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 >28 Number Hand Size (mm) Size <14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 >26 Number Genetic Variations Mutations Due to mistakes in the replication of DNA or radiation or chemicals in the environment Gene Shuffling Occurs during meiosis Genetic Variations – Mutations: Sickle Cell Anemia Sickle Cell Anemia Mutation – Harmful or Beneficial? NN – normal round blood cells NS – normal round blood cells; immune to malaria SS – sickle-celled blood cells