* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download - Los Banos Unified School District
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Sumptuary law wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Leges regiae wikipedia , lookup
Constitution of the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Conflict of the Orders wikipedia , lookup
Senatus consultum ultimum wikipedia , lookup
Roman Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
Roman Senate wikipedia , lookup
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
Early Roman army wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Augustus wikipedia , lookup
Centuriate Assembly wikipedia , lookup
History of the Constitution of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Executive magistrates of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Legislative assemblies of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
History of the Roman Constitution wikipedia , lookup
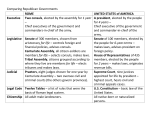
The Roman Republic Mr. Stagnaro Los Banos High School Objectives To learn about the significance of the Republic in Rome and later democracies. California Content Standards 10.1.1 - Analyze the views of law, reason and faith, and duties of the individual. 10.1.2 - Development of Western political thought Content Definition Brief History of the Republic Republican Government (not GOP) The Assembly The Senate The Consuls Roman Law Definition Republic: power rests with the citizens who have the right to elect the leaders who make government decisions (p.8). Since the Roman world was larger than one city, it became important to include people via representation instead of direct votes. Also known as an indirect democracy. The United States government is a republic. Brief History of the Republic From 753 to 509BC, Rome was ruled by Kings. It then became a Republic because the people of Rome didn't like the way that King Tarquinius had ruled. The REPUBLIC was set up to make sure that there weren't any more Tyrants in charge of Rome. In the Republic there were different parts of the Government. The Three main parts of the government were the Senate, the consuls and the Assemblies. The Republican Government: The Assembly An Assembly was a gathering of Roman citizens. Discussed new Laws Voted on Laws. The citizens also elected new senators and consuls. The rich had more votes than the other citizens so power was not shared equally. The Assembly was composed of all the plebian, the common man. The Assembly did not have a building. It was the right of the common man to assemble in the Forum and vote. Chose the 2 Consuls The Republican Government: The Senate The Senate was a bit like our Congress. People were elected by citizens and they had a discussion then voted to decide what should and should not happen. The Senate was composed of leaders from the patricians, the noble and wealthy families of ancient Rome. They controlled spending. Members of the Senate were not elected. They were chosen by the Consuls. Once chosen, they served for life. There were 300 seats in the Senate. The Republican Government: The Consuls – The highest position Two (2) elected consuls shared the head of government. Consuls were members of the Senate, who had been elected to serve for a one year term in the position of Consul The consuls most important power was that they controlled the army. Selected by the Assembly Structure of Government Under the Republic 2 Consuls Head of Government Senate (300 members) PATRICIANS PATRICIANS 1 year term Life term Consuls chose the Senators Assembly PLEBEIANS Elected the 2 Consuls Ran the government, overseeing the work of other government officials. Advised the consuls. Advised the Assembly. Directed (commanded) the army Directed spending, including tax dollars Acted as judges Approved or disapproved laws made by the Assembly Voted on laws suggested by government officials In an emergency, consuls could choose a dictator – a single ruler to make quick decisions. Made decisions concerning relationships with foreign powers Declared war or peace Both consuls had to agree on their decisions. Each had the power to Veto the other. In Latin, veto means “I forbid.” Elected government officials including judges. Roman Laws Principles All citizens had the right to equal treatment under the law A person was considered innocent until proven guilty The burden of proof rested with the accuser rather than the accused. Any law that seemed unreasonable or unfair could be set aside. The Twelve Tables: 451 BC – The rights to protection of the laws The Justinian Code: AD 528 – Collection of 5,000 laws Guide on legal matters in Western Europe Rulers and powerful people are held accountable to the law.