* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Honors Biology Notes:
Survey
Document related concepts
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Cyanobacteria wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
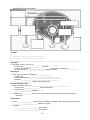
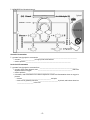
Honors Biology Notes: Unit 4 BioEnergy Metabolism and Energy • • chemistry of life is organized into ________________________________________________________ – metabolism: collection of reactions that occur in organisms; facilitated by _____________________ – two general categories of reactions: • ____________________: breakdown of macromolecules into monomers, releasing energy from the broken bonds • ____________________: building macromolecules from monomers, using energy to form bonds ATP (_________________________________________) powers cellular work – ATP loses one _____________________, producing ADP (adenosine _____________________), a phosphate group, and free energy – Any time bonds are broken; energy is _______________________ – Any time chemical bonds are made, energy is ____________ • Chemical elements essential to life are recycled in the cells by photosynthesis and cellular respiration (_________________________________________________) • ________________________ is not recycled Photosynthesis • General – plants and other autotrophs are ___________________________________ • _______________________: organisms that can make their own food rather than ingesting or absorbing it • ______________________________: organisms that use the energy of the sun to produce carbohydrates from CO2 and H2O • _______________________: organisms that are the ultimate source of organic compounds for heterotrophic organisms – ___________________________ must ingest or absorb energy from other organisms The Action Spectrum for Photosynthesis • • • • Look for the following information in the webpage: In 1883, Thomas Engelmann devised an experiment to learn __________________________________ __________________________________________________________in carrying out photosynthesis. What organism was used? _______________________________________ The wavelengths that work best for photosynthesis are ______________________________________ Chloroplasts • chloroplasts are the ______________________________________ in plants and other photoautotrophs – all _________________________________ of a plant have chloroplasts – _________________________ are the major sites of photosynthesis in most plants • about _____________________ chloroplasts per square ____________________ of leaf surface – green color comes from the __________________________________________ • chlorophyll _____________________________________________ -1- Source of Reactants •chloroplasts are found in tissue in the interior of leaves called __________________________ •carbon dioxide enters leaf (and oxygen exits) by pores in the leaf called ______________________ •water is absorbed by the _________________ and moved through the plant by veins Photosynthesis •Overall (simplified) chemical equation MEMORIZE THIS _______________________________________________________________________________ •Carbon ____________________________________________________________________________ Nova Photosynthesis Overview •MEMORIZE the following diagram! -2- 2 Major Stages of Photosynthesis •________________________________ or photochemical reaction •the _______________________________ or the thermochemical reaction or dark reactions Light Reactions General • require the energy of the sun – occurs in the ______________________________________________ of the chloroplasts – rely on two clusters of pigments with different types of chlorophyll and other pigments • ___________________________________________ (absorb different wavelengths of light) Calvin Cycle General • • • does not directly require __________________________________ – occur for only a ____________________________ after sunset, because the reactions quickly use up the __________________________________________ produced in the light reactions occurs in the __________________ of the chloroplast 3 “turns” of the Calvin Cycle are required to produce ________________________________________ Factors Affecting Photosynthesis • Light intensity – ordinary daily sunlight yields ____________________________________ of photosynthesis CO2 • – more CO2 equals a higher rate _______________________________________ • 6x CO2 can yield ________________ of photosynthesis – atmospheric CO2 has increased ___________ in last 200 years; not enough to cause great increase in photosynthesis – greenhouse effect- greater impact on ________________________________________ than rate of photosynthesis • H2O- if plant goes dry ____________________________, no CO2 taken in. • Temperature – primarily via ______________________________________- as temperature increases, rate goes up (until proteins _______________) – low temperatures (> freezing) influence both _______________________________ and “____________________” of chloroplast membrane – most plants have enzyme systems and membrane structure that are _________________________ to the temperature range they experience Cellular Respiration • • Breakdown of _____________________ (or other organic fuel) to produce energy Occurs in _________________________________________ (even those that photosynthesize) – overall (simplified reaction) (MEMORIZE) _________________________________________________________________________________ -3- MEMORIZE the following diagram! 3 phases • • • ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ Glycolysis • Glycolysis: glucose, C6H12O6 is ______________________________ – occurs in the ______________________ of the cell – products: 2 molecules of _______________________, C3H3O3 and 2 molecules of ___________ and 2 molecules of ______________________ (electron carrier) Krebs Cycle • Krebs Cycle: pyruvate is converted to __________________ – occurs in the ____________________________________________ – transfers electrons to ________________________________________ – produces: ____________________________________________ – _____________________ (oxygen requiring) process Electron Transport chain • • Electron Transport chain and ______________________________________________ – occurs on the ___________________ of the mitochondria – produces up to ________________________ – _____________________ process a maximum of ___________ molecules ATP are produced per molecule of glucose during cellular respiration Fermentation • • occurs ___________________ of Krebs Cycle and Electron Transport chain when oxygen is not present – ___________________________ : absence of oxygen Two types – _____________________________ fermentation – _____________________________ fermentation -4- • MEMORIZE the following diagram! Alcoholic Fermentation • pyruvate from glycolysis is converted to _______________________________________________ – occurs in ________________ (a fungus) and some bacteria – used to produce _______________________________________________________ Lactic Acid Fermentation • pyruvate from glycolysis is converted into ______________________________________________ – occurs in some fungi, bacteria, and __________________________________________ that have depleted stores of oxygen – used to produce ____________________________________ – in humans, cells must switch from cellular respiration to lactic acid fermentation when no oxygen is present • causes ___________________________________ and pain • lactic acid is gradually carried to ________________________ by blood, and broken down into ____________________ in the liver -5-