* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Communication Part II
Hedgehog signaling pathway wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
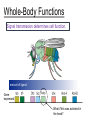
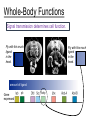
Warm-Up (12/08) On the piece of white paper from the back, answer the following question. Create a model showing a generic cell signaling pathway before and after a ligand binds to a receptor. Show how binding to a ligand regulates gene expression. Name Date Period The Endocrine System Glands release hormones (protein ligands) which travel through the body through the bloodstream. Signal-sending cell P Signal-receiving cell The Endocrine System Glands release hormones (protein ligands) which travel through the body through the bloodstream. Example: Insulin signaling Signal-receiving cell insulin P 2nd messenger Blood glucose stays low Genes encoding proteins which release glucose Cell Communication Cells can communicate… Long distance: by, for example, hormones released in the blood. Short-range: by, for example, neurotransmitters across a synapse (Thursday). Directly: by, for example, immune cells recognizing antigens on pathogens (Wednesday). Critical Thinking Question #1 Discuss this question with your partner and write or represent it. I will call on three people to share their partners’ answers. Explain why ligands can be secreted by signal-sending cells or attached to the surface of signal-sending cells. Which case would be used to send a long-distance signal? Whole-Body Functions Glycogen breaks down to release glucose. Adrenaline Hormones regulate wholebody functions. Liver Whole-Body Functions Signal transmission determines cell function. amount of ligand Gene expressed What if this was activated in the head? Whole-Body Functions Signal transmission determines cell function. Fly with this much ligand in the head. amount of ligand Gene expressed Fly with this much ligand in the head. Unicellular Functions Unicellular bacteria communicate with each other through quorum sensing. Bacterium Ligand Critical Thinking Question #2 Discuss this question with your partner and write or represent it. I will call on three people to share their partners’ answers. Patients suffering from Type I diabetes are required to take regular insulin injections to maintain low blood sugar levels. Insulin is a hormone ligand that has been proven to reduce the release of glucose from liver cells. Justify the claim that insulin causes liver cells to stop secreting glucose. Drugs work by blocking receptors. Example: blood-pressure drugs, birth-control drugs ligand Signal-receiving cell (not activated!) P drug 2nd messenger (not activated!) receptor (not activated!) Target gene (not activated!) Closure On the piece of white paper from the back, answer the following question: Explain how a drug could affect signal reception between cells and, consequently, the entire signal transduction pathway. Name Date Period Scale 1 – 10