* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Snímka 1 - TOP Recommended Websites
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
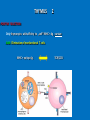
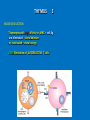
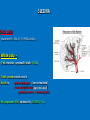
LYMPHOID ORGNS Function - maturation - differentiation - proliferation Primary (central) L.O. T and B startto express Ag - specific receptors Secondary (peripheral) L.O. Ly proliferation and differentiation after interaction with Ag Primary (central) L.O. 1) Thymus 2) Bone marrow Thymus 1 Morphology: lobular organ cortex medulla Function: maturation of T cells (only 1 x 106 of 5 x 107 tymocytov mature) Maturation: 3 STEPS: 1) Migration and proliferation 2) Differentiation 3) Selection 1) Migration and proliferation Thymocytes react with epithelial cells (cortex), dendritic cells and Mph (medulla) 2) Differentiation 1) step - 3 negat. thymocytes (CD3-,CD4-,CD8-) markers CD44+,CD25+,CD117+ TCR genes not rearranged 2) step - differentiation - TCR TCR γ markers CD44-, CD25+, CD117+ 3) thymocytes TCR γ T Ly (CD3+, CD4-, CD8-) 5% of matured T cells thymocytes TCR Th (CD3+, CD4+, CD8-) Tc (CD3+, CD4-, CD8+) THYMUS 2 POSITIVE SELECTION Only thymocytes with affinity to „self“-MHC + Ag survive AIM: Elimination of nonfunctional T cells MHC + epitop-Ag TCR/CD3 THYMUS 3 NEGATIVE SELECTION Thymocytes with high affinity to MHC + self Ag are eliminated - clonal deletion or inactivated – clonal anergy AIM: Elimination of AUTOREACTIVE T cells Secondary lymphoid organs Functions 1. Trapping and concntration of Ag 2. Production of Ab and Ag specific T cells Secondary lymphoid organs: 1. Spleen - blood born microbs and Ag 2. Lymph nodes - lymphatic pathway > skin, mucosa 3. Mucosa associated lymphatic tissue (MALT) – lining of mucosa surface Ag invading mucosa SPLEEN Function - Ab synthesis and releasing to circulation - hemokaterhesis / Tr a Er ( Structure: red pulp white pulp SLEZINA Red pulp plazma cells, Ma, Er, Tr, PMNL and Ly. White pulp (PeriArteriolar Lymphoid Sheath - PALS). T cells round central arteria B cells in primary folicules ( non stimulated) secondary folicules (Ag stimulated) germinal centre / memory cells B Ly represent 50% spleen cells, 30-40% - T Ly. Lymph node (LN) Structure - cortx - medulla Cortex Primary folicules – non activated B cells Secondary folicules - response to Ag - Activated B cels – differentiation to plasma cells - Th support B cell differentiation - dendritic cells – Ag presentation - FDC - activation of memory cells - Mph Interfolicular space and in paracortex – T cells (mainly Th) Medulla Ly, high number of Mph and dendritic cells Lymph node (LN) Ag enters LN and trapped by Mph and dendritic cells Degradation of Ag . Fragments (epitopes) are expressed on the surface of APC cells together with MHC molecules Activation of T cells The first mitotic wave in T zones is recorded 1-2 days after contact with Ag prolif. of B Ly, germinal centrers Immune system of mucosa - MALT >50% of lymphoid tissue - (GALT) gut-associated lymphoid tissues - (BALT) bronchus-associated lymphoid tissue -(GUALT) genitourinary-associated lymphoid tissue Exmples of MALT: tonsiles, appendix, Peyer`s patches, etc. … Mucosa associated lymphatic tissue - MALT Structure of MALT 1. Organized MALT (o-MALT) – immune cells in epithelial layer of mucosa and under epithelium Induction of immune reaction 2. Diffuse MALT (d-MALT) – various types of lymphoid cells (B and T Ly, Ma, Ne, Eo, Ma) in lamina propria Effector phase of immune reactions Organized MALT (o- MALT) Peyer`s patches : 1. Lymphoid folicules (> 100) central part - B Ly, FDC, DC, Ma peripheral part - T Ly 2. Epithelium - „M“ cells – transport of Ag - intra epithelia T Ly – 80% belong to CD8+ (regulatory function)