* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Lactate dehydrogenase wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
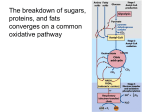
OXIDATIVE DECARBOXYLATION OF PYRUVATE Matrix of the mitochondria contains pyruvate dehydrogenase complex The fate of glucose molecule in the cell Synthesis of glycogen Glucose Glucose-6phosphate Glycogen Pentose phosphate pathway Ribose, NADPH Degradation of glycogen Gluconeogenesis Glycolysis Ethanol Pyruvate Acetyl Co A Lactate OXIDATIVE DECARBOXYLATION OF PYRUVATE Only about 7 % of the total potential energy present in glucose is released in glycolysis. Glycolysis is preliminary phase, preparing glucose for entry into aerobic metabolism. Pyruvate formed in the aerobic conditions undergoes conversion to acetyl CoA by pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex is a bridge between glycolysis and aerobic metabolism – citric acid cycle. Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex and enzymes of cytric acid cycle are located in the matrix of mitochondria. Entry of Pyruvate into the Mitochondrion Pyruvate freely diffuses through the outer membrane of mitochondria through the channels formed by transmembrane proteins porins. Pyruvate translocase, protein embedded into the inner membrane, transports pyruvate from the intermembrane space into the matrix in symport with H+ and exchange (antiport) for OH-. Conversion of Pyruvate to Acetyl CoA • Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDH complex) is a multienzyme complex containing 3 enzymes, 5 coenzymes and other proteins. Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex is giant, with molecular mass ranging from 4 to 10 million daltons. Electron micrograph of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex from E. coli. Enzymes: E1 = pyruvate dehydrogenase E2 = dihydrolipoyl acetyltransferase E3 = dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase Coenzymes: TPP (thiamine pyrophosphate), lipoamide, HS-CoA, FAD+, NAD+. TPP is a prosthetic group of B1; lipoamide is a prosthetic group of B2; and FAD is a prosthetic group of B3. The building block of TPP is vitamin B1 (thiamin); NAD – vitamin B5 (nicotinamide); FAD – vitamin B2 (riboflavin), HS-CoA – vitamin B3 (pantothenic acid), lipoamide – lipoic acid Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex is a classic example of multienzyme complex Overall reaction of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex The oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate catalized by pyruvate dehydrogenase complex occurs in five steps.