* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Antibodies - INAYA Medical College
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Gluten immunochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Immunoprecipitation wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Guillain–Barré syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Complement system wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Autoimmune encephalitis wikipedia , lookup
Duffy antigen system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
Anti-nuclear antibody wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
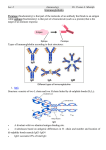
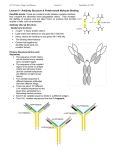
CLS 441 Characteristics of blood group antibodies: • Classification of Blood Group Antibodies – Antigen - Immunologlobulin - Antibody - Hemoglobin - Anti Human globulin - Indirect Antiglobulin Test - Direct Antiglobulin Test - Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia. - Hemolytic Disease of New born - Adenosine Triphosphate - Citrate phosphate dextrose - Ethyldiamine Tetra Acetic acid - Acid Citrate dextrose - Molecular weight - Rhesus • Immunohematology is one of the specialized branches of medical science. • It deals with the concepts and clinical techniques related to Modern Transfusion Therapy. • Merges aspects of hematology, immunology & genetics. • Serologic, genetic, biochemical and molecular study of antigens associated with membrane structures on the cellular constituents of the blood Antigens Antigens: biological substance when introduce to foreign circulation , it stimulate the immune response to produce specific Antibody. antigen may also be formed inside the body such as ABO antigen belong to protein called Immunoglobulin produced by plasma cells react with Ag corresponding “ specifically” • IgG : with heavy chains gamma (γ). • IgA: with heavy chains alpha (α) • IgM: with heavy chains mu (μ) • IgD: with heavy chains delta(δ ) • IgE: with heavy chains epsilon(Є) IgG, IgM and IgA. It is a Y-shaped molecule made of 2 heavy chains & 2 light chains. Antibody Antigen Characteristics of blood group antibodies: IgG: • Is the predominant immunoglobulin in normal serum. • Accounting for about 85% of the total immunoglobulin • Is the only immunoglobulin to be transferred from mother to fetus. • Is the smallest antibody which has a MW of 150,000 Dalton • Is capable of binding complement. • Is predominantly produced during the secondary immune response. IgM: • Accounts for about 10% of the immunoglobulin pool. • Is the predominant antibody produced in a primary immune response. • and has the largest MW of 900,000. • Because of its large size IgM cannot pass the placental barrier to the fetus. • Is complement binding. IgA: • Ig A with a MW of 160,000 constitutes 10 to 15 % of the total circulatory immunoglobulin pool. • Is the predominant immunoglobulin in secretions such as, tears, saliva, colostrum, breast milk, and intestinal secretions. Type of Antibodies • Based on their development, blood group antibodies are classified into Natural and Immune antibodies. 1-Natural antibodies: • Are red cell antibodies in the serum of an individual that are not stimulated by previous red cell sensitization. Characteristics. • Exhibit optimum in vitro agglutination. sometimes referred to as complete antibodies. • Give optimum reaction at a temperature of room or lower, and they are also called cold agglutinins. • These antibodies are of high MW that they can’t cross the placental barrier, eg. IgM. 2- Immune antibodies: Are antibodies stimulated by either transfusion or pregnancy, i.e. as a result of immunization by red cells. • Characteristics – Do not exhibit visible agglutination of saline- suspended erythrocytes, and called incomplete antibodies – React optimally at a temperature of 37C, and are so called warm agglutinins. – These antibodies can cross the placental barrier, e.g. IgG 1. Alloantibodies:• Reacts with foreign Ag not present on patient’s own RBC • Most produced as result of immune stimulation via transfusion or pregnancy (usually during delivery) 2. Autoantibodies:• Reacts with an Ag on patient’s own cells & with that same Ag on the cells of other individuals Antigen and Antibody Reactions Type of reaction 1-Sensitization: simple combination between red cell antigen and corresponding antibody in a vivo or vitro without visible agglutination. 2-Hemoagglutiation: reaction between red cell bound antigen and corresponding antibody with visual agglutination. 3-Hemolysis: Reaction between red cell bound antigen and antibody with complement fixation resulting in releases of hemoglobin. 4-Neutralization (inhibition): Reaction between red cell antigen and corresponding antibody both in soluble state with precipitation. Is the reaction of soluble Ag with soluble Ab. The reaction results in the formation of Ag-Ab complexes (lattices) Antigen Antibody • Complete or incomplete, cold or warm, natural or immune types of antibodies. • Amount of antibody. • Amount of antigen. • Avidity of antibody. • PH of the reaction. • Temperature of the reaction. • Incubation time. • Saline concentration. • Type of additive (protein, enzyme). • Speed and time of centrifugation.