* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ch-4-earth-chemistry
Bent's rule wikipedia , lookup
Computational chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Oxidation state wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical potential wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Metastable inner-shell molecular state wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Molecular Hamiltonian wikipedia , lookup
Chemical element wikipedia , lookup
Condensed matter physics wikipedia , lookup
Livermorium wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Low-energy electron diffraction wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Periodic table wikipedia , lookup
Auger electron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
Hypervalent molecule wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Extended periodic table wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Electronegativity wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital diagram wikipedia , lookup
Resonance (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Bond valence method wikipedia , lookup
Metallic bonding wikipedia , lookup
Atomic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
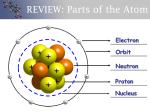
Earth Chemistry Ch. 4 Notes Ch. 4 S. 1 Matter What about Mendeleev’s work makes him stand out among other scientists of his time? How was his work unique when compared to others who were doing similar research? Properties of Matter Matter – Anything that takes up space and has mass. Two types of distinguishing characteristics: Physical Properties – can be observed without changing the chemical composition of the substance. EX: Color, Shape, Boiling Point, Melting Point, Malleability, luster, state of matter, scent, size Chemical Properties – Describe how a substance reacts with other substances. Ex: how or if a substance reacts with water, or an acid, or oxygen. http://my.hrw.com/sh2/sh07_10/student/flash/visual_concepts/75013.h tm Write down some Physical Properties of the object Baking Soda Properties Sort the properties into Chemical and Physical properties Properties list Reacts with vinegar to produce CO2 White solid powder Not Flammable Decomposed by acids Tastes salty Density = 2.20 g/cm3 Odorless Chemical Physical Baking Soda Properties Sort the properties into Chemical and Physical properties Properties list Chemical Physical Reacts with vinegar to produce CO2 White solid powder Not Flammable Decomposed by acids Tastes salty Density = 2.20 g/cm3 Odorless Elements Element: A substance that cannot be separated or broken down into simpler substances by chemical means. Each element is defined by unique physical and chemical properties that can define it. http://my.hrw.com/sh2/sh07_10/student/flash/visual_concepts/75006.htm Atomic Structure Proton – A subatomic particle that has a positive charge and is located in the nucleus The number of protons = atomic number Neutron – A subatomic particle that has no charge and is located in the nucleus Electron – A subatomic particle that has a negative charge and is located in the nucleus. Nucleus – A small region in the center of the atom. Does the nucleus have a positive or negative or neutral charge? Electron Cloud – The area around the nucleus where the electrons are located. Why do the electrons not fly off into space? Why do they continue to travel around the nucleus? Label the Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons, nucleus, and electron cloud. Atomic Number & Atomic Mass Atomic Number: the number of protons in the nucleus of the atom. Does the atomic number equal the number of electrons in an uncharged atom? Atomic Mass: The sum of the number of protons and neutrons in an atom. The mass of an electron is so small, that it is not included in the mass of the atom. The mass of 1 proton = the mass of 1,840 electrons Isotopes & Average Atomic Mass Isotope: One of two or more atoms that have the same number of protons (atomic numbers), but different numbers of neutrons (atomic mass) Remember atoms are characterized by their atomic numbers. Having a different number of neutrons or atomic mass would not change the atom into a different element. It just changes the atomic mass. Average Atomic Mass: The average of mass of all known isotopes of an element. Assign the following labels Labels Average Atomic Mass Atomic Number # of Protons # of Protons and neutrons Fill in the concept map Word List: Neutrons Atomic Number Electrons Atoms Atomic Mass Isotope Valence Electrons and Periodic Properties Elements are arranged in columns, which are called groups. Valence Electrons – the outermost electrons in an electron cloud. The chemical properties of an element are largely determined by the valence electrons. Within each group (or column) the atoms generally have the same number of valence electrons. Groups 1 – 2 : atoms have the same number of valence electrons as the group number Groups 3 -12: 2 or more valence electrons Groups 13 – 18: valence electrons = group # - 10 Group18: 8 valence electrons = Stable, unreactive. All atoms “want” to have 8 valence electrons. Atoms are seeking stability. Elements with only 1-3 valence electrons (mostly metals) , lose electrons easily. 4 – 5 valence electrons (Non-metals) gain electrons easily. Valence Electrons and Periodic Properties Groups 1 – 2 : atoms have the same number of valence electrons as the group number Groups 3 -12: 2 or more valence electrons Groups 13 – 18: valence electrons = group # - 10 Group18: 8 valence electrons = Stable, unreactive. Elements with only 1-3 valence electrons (mostly metals) , lose electrons easily. 4 – 5 valence electrons (Non-metals) gain electrons easily. Ch.4 S .2 Combinations of Atoms Compound – A substance that is made up of two or more atoms of elements joined by chemical bonds Ex: H2O, CO, CO2, CoI3 Molecule – The smallest unit of a compound that can exist by itself and retain all of the compound’s chemical properties. Example: Oxygen – always found as at least O2 , never any less Chemical Formulas Chemical formula – a combination of letters and numbers that shows which elements make up a compound. Also, shows the numbers of atoms of each element required to make up a molecule of a compound. H2O How many atoms of hydrogen are in a molecule of water? How many atoms of a oxygen are in a molecule of water? Chemical Equations Reactions of the elements and compounds are described using a chemical equation EX: CH4+2O2→CO2+2H2O “One molecule of methane reacts with 2 molecules of Oxygen to make one molecule of carbon dioxide and 2 molecules of hydrogen” Balancing Chemical Equations You cannot change the chemical formulas or the subscripts – ONLY THE COEFFICIENTS Balance the formula by adding to the coefficients. EX: H2+ O2 + H2O Try this one: Magnesium gas, Mg, reacts with Oxygen gas, O2 to form MgO. Write a balanced equation for the reaction. Chemical Bonds Chemical Bonds: The forces that hold chemicals together Electrons involved in bonding are only the valence electrons Ion: A particle or atom that carries a charge Example: A neutral sodium atom has a charge of zero (equal # of protons and neutrons) and only 1 valence electron. Once it loses that valence electron, it will have 8 valence electrons and be stable and most likely, not gain or lose anymore electrons. What would be the charge on a sodium atom that loses one electron? Chemical Bonds Ionic Bond: The attractive force between oppositely charged atoms, which form when electrons are transferred between atoms or molecules EX: NaCl How many valence electrons does a neutral sodium atom have? How many valence electrons does a neutral chloride atom have? What do you think will happen when the two come into contact with one another? Chemical Bonds Covalent bond: A bond that is formed when atoms share one or more pairs of electrons. EX: Cl2 How many valence electrons does a neutral chloride atom have? If two chloride atoms came together, could they give or donate electrons as that they both have 8 valence electrons? Chemical Bonds Polar Covalent Bonds: Covalent bonds that do not share electrons equally Ex: H2O The oxygen attracts the electrons more strongly than the hydrogen, so the electrons tend to be more crowded near the oxygen end. In a molecule of H2O, which area is more negative (The hydrogens or the oxygen)? Which area is more positive? Why? Chemical Bonds Mixtures Mixture: A combination of two or more substances that are not chemically combined. Heterogeneous: mixtures in which two more substances are not uniformly distributed You can easily identify the different parts in this mixture Homogeneous: A homogeneous mixture has the same composition and properties throughout. This is also called a solution. You cannot easily identify the parts that make up the mixture. Write down an example of a heterogeneous mixture and homogeneous mixture Is Milk a mixture? Review What is the difference between an ionic bond and covalent bond? What is a compound? What is the difference between a compound and a mixture? Do the chemical properties of the components of a mixture stay the same or change? Balance the equation: N2+ H2 → NH3