* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
5-HT3 antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of antiandrogens wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of angiotensin receptor blockers wikipedia , lookup
NMDA receptor wikipedia , lookup
Toxicodynamics wikipedia , lookup
5-HT2C receptor agonist wikipedia , lookup
NK1 receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Cannabinoid receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
59-291 Section 2, Lecture 2
Cholinergic Receptor Agonists
Muscarinic Receptors
-smooth muscle
-cardiac tissue parasymp.
-glands
neuroeffector junctions
CNS- presynaptic parasymp. and symp. nerves and autonomic ganglia
-activation of muscarinic receptors on presynaptic autonomic nerves
inhibits further neurotransmission.
-muscarinic receptors on symp. nerve terminals provides for
communication between parasymp. and symp. nervous systems
release of acetylcholine from parasymp nerves inhibits the release1 of
NE from symp. Nerves.
-5 types of muscarinic receptors M1-M5
Principal types M1,M2 M3
Type of Receptor
Principal Locations
Mechanism of Signal Transduction
Effects
M1 ("neural")
Autonomic ganglia, presynaptic
nerve terminals, and central
nervous system
Increased inositol triphosphate (IP3) and
diacylglycerol (DAG)
Modulation of neurotransmission
M2 ("cardiac")
Cardiac tissue (sinoatrial and
atrioventricular nodes)
Increased potassium efflux or decreased
cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP)
Slowing of heart rate and conduction
M3 ("glandular")
Smooth muscle and glands
Increased IP3 and DAG
Contraction of smooth muscles and
stimulation of glandular secretions
Vascular smooth muscle
Increased cyclic guanosine monophosphate
(cGMP) due to nitric oxide stimulation
Vasodilation
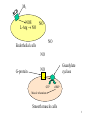
Muscarinic
Signal transduction:
-Smooth muscle & glands: M1 and M3 via G-proteins: increased
IP3 and DAG
-Vascular Smooth Muscle (endothelial cells): M3 turns on nitric
2
oxide synthase (NOS)
M3
NOS
NO
L-Arg NO
NO
Endothelial cells
NO
G-protein
Guanlylate
cyclase
NO
GTP
cGMP
Muscle relaxation
Smooth muscle cells
3
-M2 increases K+ efflux and destruction of cAMP via increase in cyclic
nucleotide phosphodiesterase activity
Nicotinic Receptors
Found at all autonomic ganglia, somatic neuromuscular junctions and
CNS
-ligand-gated sodium channels
-autonomic ganglia activation of nicotinic receptors produces neuronal
excitation leading to the release of neurotransmitters at postganglionic
neuroeffector junctions
-at neuromuscular junctions activation leads to depolarization and the
release of Ca2+ from the sarcoplasmic reticulum which results in
muscle contraction.
4
Principal Locations
Mechanism of Signal
Transduction
NM (in muscles)
Somatic neuromuscular
junctions
Increased sodium
influx
Contraction of muscles
NN (in neurons)
Autonomic ganglia
Increased sodium
influx
Excitation of postganglionic neurons
Type of Receptor
Effects
Nicotinic
5
Cholinergic receptor agonists
• Direct acting agonists
– bind and activate cholinergic receptors
• Indirect-acting agonists
– increase synaptic [ACh] by either inhibiting
AChE or increasing the release of ACh from
terminals
6
Direct acting
Choline esters
Drug
Receptor Specificity
Hydrolyzed by Cholinesterase
Route of Administration
Clinical Use
Yes
Intraocular
Miosis during ophthalmic surgery
Intracoronary
Coronary angiography
Choline esters
Acetylcholine
Muscarinic and
nicotinic
Bethanechol
Muscarinic
No
Oral or subcutaneous
Postoperative or postpartum
urinary retention
Carbachol
Muscarinic and
nicotinic
No
Topical ocular
Glaucoma
Intraocular
Miosis during ophthalmic surgery
ACh- rapidly hydrolyzed
Effects and indicators:
-intraocular use during cataract
surgery where it produces miosis
-in diagnostic angiography injected
directly into coronary artery to
7
produce vasodiation (M3-receptors)
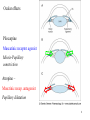
Ocular effects
Pilocarpine
Muscarinic receptor agonist
Miosis-Pupillary
constriction
Atropine –
Muscrinic recep. antagonist
Pupillary dilatation
8
Direct acting plant alkaloids
Drug
Receptor Specificity
Hydrolyzed by
Cholinesterase
Route of Administration
Clinical Use
Plant alkaloids
Muscarine
Muscarinic
No
None
None
Nicotine
Nicotinic
No
Oral or transdermal
Smoking cessation programs
Pilocarpine
Greater affinity for muscarinic than for
nicotinic
No
Topical ocular
Oral
Glaucoma
Xerostomia
Muscarine- source mushrooms
NicotineIndications: muscarine no current medical use; nicotine as dermal
patches in smoking cessation programs
Pilocarpine- source pilocarpus a shrub
Effects and indications:
Tratment of open-angle glaucoma
9
10
Indirect acting cholinergic agonists
Reversible AChe inhibitors
Carbamates- slow hydrolysis compared to ACh
11
12
Irreversible inhibitors
phosphoesters
13
Practice question
• What is the mechanism of signal
transduction of the following receptors
• M1 (neuronal)
– Increased IP3 and DAG
• M2 (Cardiac)
– Increased potassuim efflux or decrease cGMP
• NM( in muscles)
– Increased soduim influx
14
•
•
•
What is the difference between directacting cholinergic agonists and indirectacting agonists
Direct-acting agonist: bind and activate
cholinergic receptors
Indirect-acting receptors: increase the
synaptic concentration of Ach
15